Summary
Voltage, membrane current and contraction were simultaneously measured in voltage clamp experiments (single sucrose gap) on cat ventricular trabeculae. The pulse programs allowed the determination of the potential dependence of the steady state activation and inactivation as well as the restoration of the calcium-carrying system (slow inward current).
-
1.
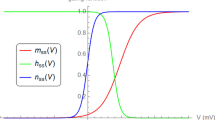
The steady state activation variable (d ∞) rose in a sigmoid manner from −50 mV (d ∞ nearly 0) to 0 mV (d ∞ nearly 1). The experimental values can be described by the function 1/1 + exp [(V h −V)/S] where half activation (V h )=−22.5 mV andS=7.6 mV.
-
2.
The steady state inactivation variable (f ∞) declined from 1 at −60 mV to 0 at + 10 mV. The best fit curve is nearly a mirror image of the activation curve withV h =−28 mV andS=−8.3 mV.
-
3.
The voltage dependence of the (normalized) peak tension was well described by the steady conductance variables except at potentials positive to +20 mV.
-
4.
A “steady state” tension (superimposed on “tonic tension”) was found in the potential range where a steady state conductance is predicted by the curves describing steady state activation and inactivation.
-
5.
Following inactivation, the time courses of restoration of the calcium-carrying system and tension were identical. Time courses were exponential with τ=118 msec at −80 mV, 144 msec at −60 mV, and 198 msec at −40 mV.
-
6.
Two possible models of excitation-contraction coupling in line with the present results are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoni, H., Jacob, R., Kaufmann, R.: Mechanische Reaktionen des Frosch- und Säugetiermyokards bei Veränderungen der Aktionspotential-Dauer durch konstante Gleichstromimpulse. Pflügers Arch.306, 33–57 (1969)
Armstrong, C. M., Bezanilla, F.: Currents related to movements of the gating particles of the sodium channels. Nature (Lond.)242, 459–461 (1973)
Bassingthwaighte, J. B., Reuter, H.: Calcium movements and excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac cells. In: Electrical phenomena in the heart, W. C. DeMello, ed., pp. 353–395. New York: Academic Press 1972
Beeler, G. W., Jr., Reuter, H.: Voltage clamp experiments on ventricular myocardial fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)207, 165–190 (1970a)
Beeler, G. W., Jr., Reuter, H.: Membrane calcium current in ventricular myocardial fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)207, 191–209 (1970b)
Beeler, G. W., Jr., Reuter, H.: The relation between membrane potential, membrane currents and activation of contraction in ventricular myocardial fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)207, 211–229 (1970c)
Birks, R. I., Davey, D. F.: Osmotic responses demonstrating the extracellular character of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Physiol. (Lond.)202, 171–188 (1969)
Birks, R. I., Davey, D. F.: An analysis of volume changes in the T-tubes of frog skeletal muscle exposed to sucrose. J. Physiol. (Lond.)222, 95–111 (1972)
Brown, H. F., Noble, S.: Membrane currents underlying delayed rectification and pacemaker activity in frog atrial muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)204, 717–736 (1969)
Caputo, C.: The effect of low temperature on the excitation-contraction coupling phenomena of frog single muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)223, 461–482 (1972)
Carey, M. J., Conway, E. J.: Comparison of various media for immersing frog sartorii at room temperature, and evidence for the regional distribution of fibre Na+. J. Physiol. (Lond.)125, 232–250 (1954)
Endo, M., Janaka, M., Ogawa, Y.: Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature (Lond.)228, 34–36 (1970)
Fabiato, A., Fabiato, F.: Excitation-contraction coupling of isolated cardiac fibres with disrupted or closed sarcolemmas. Circulat. Res.31, 293–307 (1972)
Fawcett, D. W., McNutt, N. S.: The ultractructure of the cat myocardium. J. Cell. Biol.42, 1–45 (1969)
Ford, L. E., Podolsky, R. J.: Intracellular calcium movements in skinned muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)223, 21–33 (1972)
Forssmann, W. G., Girardier, L.: A study of the T-system in rat heart. J. Cell. Biol.42, 1–19 (1970)
Gordon, A. M., Godt, R. E.: Some effects of hypertonic solutions on contraction and excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscles. J. gen. Physiol.55, 254–275 (1970)
Harris, E. J.: Distribution and movement of muscle chloride. J. Physiol. (Lond.)166, 87–109 (1963)
Heistracher, P., Hunt, C. C.: The relation of membrane changes to contraction in twitch muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)201, 589–612 (1969a)
Heistracher, P., Hunt, C. C.: Contractile repriming in snake twitch muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)201, 613–626 (1969b)
Hodgkin, A. L., Horowicz, P.: Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)153, 386–403 (1960)
Hodgkin, A. L., Huxley, A. F.: The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon ofLoligo. J. Physiol. (Lond.)116, 497–506 (1952)
Kerrick, W. G. L., Best, P. M.: Calcium ion release in mechanically disrupted heart cells. Science183, 435–437 (1974)
Morad, M., Goldman, Y.: Excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle: membrane control of development of tension. Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol.27, 257–313 (1973)
New, W., Trautwein, W.: Inward membrane currents in mammalian myocardium. Pflügers Arch.334, 1–23 (1972a)
New, W., Trautwein, W.: The ionic nature of slow inward current and its relation to contraction. Pflügers Arch.334, 24–38 (1972b)
Noble, D., Tsien, R. W.: Outward membrane currents, activated in the plateau range of potentials in cardiac Purkinje fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)200, 205–231 (1969)
Ochi, R., Trautwein, W.: The dependence of cardiac contraction on depolarization and slow inward current. Pflügers Arch.323, 187–203 (1971)
Reuter, H.: Time and voltage-dependent contractile responses in mammalian cardiac muscle. Europ. J. Cardiol.1/2, 177–181 (1973)
Rogus, E., Zierler, K. L.: Sodium and water contents of sarcoplasm and sarcoplasmic reticulum in rat skeletal muscle: effects of anisotonic media, ouabain and external sodium. J. Physiol. (Lond.)233, 227–270 (1973)
Schneider, M. F., Chandler, W. K.: Voltage-dependent charge movement in skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature (Lond.)242, 244–246 (1973)
Shine, K. I., Langer, G. A.: Caffeine effects upon contraction and calcium exchange in rabbit myocardium. J. molec. cell. Cardiol.3, 255–270 (1971)
Washio, H.: Effect of external calcium and of temperature on contraction in snake muscle fibers. J. gen. Physiol.63, 415–431 (1974)
Winegrad, S.: The intracellular site of calcium activation of contraction in frog skeletal muscle. J. gen. Physiol.55, 77–88 (1970)
Wood, E. H., Heppner, R. L., Weidmann, S.: Inotropic effects of electric currents. I. Positive and negative effects of constant electric currents or current impulses applied during cardiac action potentials. II. Hypothesis: Calcium movements, excitation-contraction coupling and inotropic effects. Circulat. Res.24, 409–445 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, SFB 38 “Membranforschung” Projekt G1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trautwein, W., McDonald, T.F. & Tripathi, O. Calcium conductance and tension in mammalian ventricular muscle. Pflugers Arch. 354, 55–74 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584503
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584503