Summary
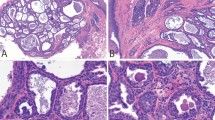
Dysgenetic (bilateral) polycystic parotid glands present a rare pathological picture which has not yet been described in detail. In the Salivary Glands Register (Institute of Pathology, University of Hamburg) 360 non-tumourous cysts were registered (from a total of 5739 cases of disturbances of the salivary glands for the years 1965–1979). Among them there were 2 cases of polycystic parotid glands. The analysis of the observations in these cases led to the following conclusions concerning polycystic parotid glands:
-
1.
The disease may be unilateral or bilateral. The cysts, which are not uniform in size, are bounded by duct epithelia exhibiting various sorts of differentiation (striated duct and intercalated duct epithelium, primitive epithelial buds) and containing secretion products, spheroliths and microliths. Regressive focal epithelial alterations with desquamation occur. The remains of the glandular parenchyma can be found among the cysts.
-
2.
The cystic change is due to a developmental malformation of the duct system, in particular a disturbance of ramification and canalization. Evidence for this conclusion can be found in the spur-like septation of the cysts and the hourglasslike indentations.
-
3.
Polycystic parotid glands can be compared with cystic malformations of the pancreas (cystic pancreas) or the lung (cystic lung).
-
4.
This disease must be distinguished from congenital sialectasias of the parotid glands, from cysts of the salivary ducts and from lymphoepithelial cysts. The criteria for differential diagnosis are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo A, Nelson JF (1971) Lymphoepithelial cysts of the oral cavity. Report of nine cases. Oral Surg 31:632–636
Becker V (1973) Bauchspeicheldrüse (Inselsystem ausgenommen). In: Doerr W, Seifert G, Uehlinger E (eds) Spezielle pathologische Anatomie, vol. 6. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Becker W, Haubrich J, Seifert G (1978) Krankheiten der Kopfspeicheldrüsen. In: Berendes J, Link R, Zöllner F (eds) Hals-Nasen-Ohren-Heilkunde in Praxis und Klinik, vol 3, 12. Thieme, Stuttgart, S 1–55
Bernier JL, Bhaskar SN (1958) Lymphoepithelial lesions in salivary glands. Histogenesis and classification based on 186 cases. Cancer 11:1156–1179
Bhaskar SN (1966) Lymphoepithelial cysts of the oral cavity. Report of twenty-four cases. Oral Surg 21:120–128
Bolck F, Machnik G (1978) Leber und Gallenwege. In: Doerr W, Seifert G, Uehlinger E (eds) Spezielle und pathologische Anatomie, vol 10. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Donath K, Dietrich H, Seifert G (1978) Entwicklung und ultrastrukturelle Cytodifferenzierung der Parotis des Menschen. Virchows Arch A Path Anat and Histol 378:297–314
Giese W (1960) Die Atemorgane. In: Kaufmann E. Staemmler M (eds) Lehrbuch der speziellen Pathologischen Anatomie 11./12. ed, vol II/3. De Gruyter, Berlin, p 1417–1974.
Giunta J, Cataldo E (1973) Lymphoepithelial cysts of the oral mucosa. Oral Surg 35:77–84
Gorlin RJ (1970) Cysts of the jaws, oral floor, and neck. In: Gorlin RJ, Goldman HM (eds) Thoma's oral pathology. 6th ed, vol 1. Mosby, St. Louis, p 445–480
Harrison JD (1975) Salivary mucoceles. Oral Surg 39:268–278
Haubrich J (1976) Klinik der nichttumorbedingten Erkrankungen der Speicheldrüsen. Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryng 213:1–59
Mihalyka EE (1962) Congenital bilateral polycystic parotid glands. J Am Med Ass 187:154–155
Moore T (1940) Cangenital cysts of the parotid gland. Lancet 1:168–170
Östör AG, Fottune DW (1978) Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformations of the lung. Am J Clin Path 70:595–604
Potter EJ (1972) Normal and abnormal development of the kidney. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago
Rauch S, Gorlin RJ, Seifert G (1970) Diseases of the salivary glands. In: Gorlin RJ, Goldman HM (eds) Thoma's oral pathology, 6th ed, vol 2. Mosby, St. Louis, p 962–1070
Richardson GS, Clairmont AA, Erickson ER (1978) Cystic lesions of the parotid gland. Plast Reconstr Surg 61:364–370
Seifert G (1956) Die Pathologie des kindlichen Pankreas. Thieme, Leipzig
Seifert G (1966) Mundhöhle, Mundspeicheldrüsen, Tonsillen und Rachen. In: Doerr W, Uehlinger E (eds) Spezielle pathologische Anatomie, vol 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Seifert G (1980) Lymphoid lesions of the oral cavity. Path Res Pract 167:179–203
Seifert G, Donath K (1976) Die Morphologie der Speicheldrüsenerkrankungen. Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryng 213:111–208
Seifert G, Bull HG, Donath K (1980 a) Histologic subclassification of the cystadenolymphoma of the parotid gland. Analysis of 275 cases. Virchows Arch A Path Anat and Histol 388:13–38
Seifert G, Donath K, Gumberz Chr v (1980b) Granulomatöse Reaktionen der Speicheldrüsen. Klassifikation und Pathogenese. Verh Dtsch Ges Path 64:250–256
Seifert G, Waller D (1981) Klassifikation der Parotiszysten. Differentialdiagnose der Speichelgangzysten und lymphoepithelialen Zysten. Laryng Rhinol 60: in press
Thackray AC, Lucas RB (1974) Tumors of the major salivary glands. Atlas of tumor pathology, second series, fasc 10. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington
Thomsen St (1980) Die dysgenetische (bilaterale) Cystenparotis. Morphologische Analyse und Differentialdiagnose einer seltenen Speicheldrüsenkrankheit. Diss, Hamburg
Weitzner St (1973) Abbreviated case report. Lymphoepithelial (branchial) cyst of parotid gland. Oral Surg 35:85–88
Young JA, Lennep EW van (1978) The morphology of salivary glands. Academic Press, London New York San Francisco
Zollinger HU (1966) Niere und ableitende Harnwege. In: Doerr W, Uehlinger E (eds) Spezielle pathologische Anatomie, vol 3. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. H. Bredt, Mainz on the occasion of his 75th birthday
Supported by the Tumor Center Hamburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seifert, G., Thomsen, S. & Donath, K. Bilateral dysgenetic polycystic parotid Glands. Virchows Arch. A Path. Anat. and Histol. 390, 273–288 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496559
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00496559