Summary
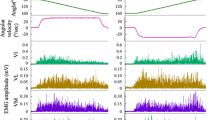
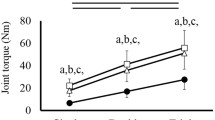
The physiological features of two antagonistic muscle groups, the dorsiflexors (DF) and plantarflexors (PF) of the ankle, have been compared in 46 healthy subjects (31 men and 15 women) aged 19–65 years. The DF muscles, of which tibialis anterior (TA) was studied most thoroughly, had relatively small twitches, with moderately fast contraction and relaxation phases, and had marked post-activation potentiation; they were susceptible to fatigue during isometric exercise. The PF muscles had comparatively large twitches, with slow contraction and relaxation phases, and poor post-activation potentiation; they were more resistant to fatigue. Women differed from men in having smaller TA twitches and slower PF twitches; PF twitches were also slower in older subjects. The marked differences in physiological properties between DF and PF muscles contrasted with relatively modest histochemical differences found by ourselves and others.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barcroft H, Millen J (1939) The blood flow through muscle during sustained contractions. J Physiol (Lond) 97: 17–22
Belanger AY, McComas AJ (1981) Extent of motor unit activation during effort. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 51: 1131–1135
Bigland B, Lippold OC (1954) Relationship between force, velocity and integrated electrical activity in human muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 123: 214–224
Bigland-Ritchie B (1982) EMG and fatigue of human voluntary and stimulated contractions. In: Porter R, Whelan J (eds) Human muscle fatigue: physiological mechanisms (Ciba Foundation Symposium). Pitman Medical, London pp 130–148
Brown GL, Von Euler US (1938) The after effects of a tetanus on skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 93: 39–60
Buchthal F, Schmalbruch H (1970) Contraction times and fiber types in intact human muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 79: 435–452
Close R, Hoh FFY (1968) The after-effects of repetitive stimulation on the isometric twitch contraction of rat fast skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 197: 461–477
Desmedt JE, Hainaut K (1968) Kinetics of myofilament activation in potentiated contraction: staircase phenomenon in human skeletal muscle. Nature (Lond) 217: 529–532
Edström L, Nyström B (1969) Histochemical types and sizes of fibres in normal human muscles. Acta Neurol Scand 45: 257–269
Edwards RHT, Hill DK, Jones DA, Merton PA (1977) Fatigue of long duration in human muscle after exercise. J Physiol (Lond) 272: 257–269
Larsson L (1978) Morphological and functional characteristics of ageing skeletal muscle in man. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 457: 36
Marsh E, Sale D, McComas AJ, Quinlan J (1981) The influence of joint position on ankle dorsi-flexion in man. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 51: 160–167
Merton PA (1954) Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol (Lond) 124: 553–564
McComas AJ (1977) Neuromuscular Function and Disorders. Butterworths, London pp 51–54
Sale D, Quinlan J, Marsh E, McComas AJ, Belanger AY (1982) Influence of joint position on ankle plantarflexion in humans. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 52: 1636–1642
Thorstensson A (1976) Muscle strength, fiber types and enzyme activities in man. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 443: 45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by financial aid from the Muscular Dystrophy Association of Canada
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belanger, A.Y., McComas, A.J. & Elder, G.B.C. Physiological properties of two antagonistic human muscle groups. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 51, 381–393 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00429075
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00429075