Summary
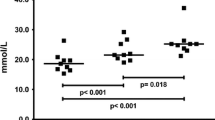
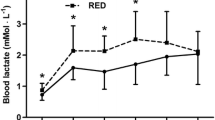
Nine female athletes were examined before and after a 25 km race (German championship). Their average running speed was 3.89 m/s. Postexercise weight loss was 1.60±0.58 kg or 2.87% of body weight, the mean rectal temperature increased by 1.04±0.52‡ C to 38.4±0.54‡ C. Leucocytes, but no other blood parameters (hemoglobin, hematocrit, erythrocytes, MCV) showed a marked rise after the race. Blood lactate rose from 1.86±0.34 to 4.97±1.19 mmol/l but hypoglycemia was not present in any of the athletes at the end of exercise. After the run serum enzymes showed lower increases than those observed in men for the same exercise duration. Serum sodium, chloride and potassium showed similar increases, inorganic phosphate higher increments than found in men. The comparatively high rise in free glycerol suggested a marked mobilization of lipid substrate, whereas the increment in serum of free fatty acids was lower than in male subjects after similar athletic events.
A lowering of neuromuscular excitability (m. vastus medialis quadricipitis) was found after the race but the changes were significant only for the fibers responding to longer durations of stimuli (0.3–30 ms).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bass A, Vondra K, Rath R, Vitek V (1975) M. Quadriceps femoris of man, a muscle with an unusual enzyme activity pattern of energy supplying metabolism in mammals. Pflügers Arch 345: 249–255
Berg A, Haralambie G (1978) Changes in serum creatine kinase and hexose phosphate isomerase activity with exercise duration. Eur J Appl Physiol 39: 191–201
Berg A, Haralambie G (1979) VerÄnderungen verschiedener energieliefernder Substrate im Blut bei Ausdauerbelastungen von Frauen. Med Welt 18: 703–706
Berg A, Keul J (1979) Energiestoffwechsel bei körperlicher Arbeit. Phlebol Proktol 8: 213–220
Costill DL, Fink WJ, Getchell LH, Ivy JL, Witzmann FA (1979) Lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle of endurance-trained males and females. J Appl Physiol: Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 47: 787–791
Davis JA, Vodak P, Wilmore JH, Vodak J, Kurtz P (1976) Anaerobic threshold and maximal aerobic power for three modes of exercise. J Appl Physiol 41: 544–550
Drinkwater B (1973) Physiological responses of woman to exercis. In: Wilmore JH (eds) Exercise and sport sciences reviews, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 125–153
Elliot B, Wilkinson J (1963) The serum “α-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase” in diseases other than myocardial infarction. Clin Sci 24: 343–355
Fischer E, Licht S (1971) Electrodiagnosis and electromyography. Waverly-Press, Baltimore, pp 66–112
Götz A (1974) Einfache, radiale Immundiffusion (RID) zur quantitativen Plasmaproteinbestimmung. In: Englhardt A, Lommel H (eds) Serumproteine. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 15–25
Haralambie G, Berg A (1976) Serum urea and amino acid nitrogen changes with exercise duration. Eur J Appl Physiol 36: 39–48
Haralambie G (1978) StoffwechselverÄnderungen nach langdauernder körperlicher Belastung beim Menschen. Wiss Abt Fresenius KG, Bad Homburg
Haralambie G, Berg A (1979) VerÄnderungen physiologischer und biochemischer Grö\en nach Ausdauerbelastung bei Frauen mit und ohne Kalziumsubstitution. Med Welt 30: 1233–1238
Haralambie G (1979) Skeletal muscle enzyme activities in female subjects of various ages. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir 15: 259–267
Haralambie G, Senser L (1980) Metabolic changes in man during long-distance swimming. Eur J Appl Physiol 43: 115–125
Israel S (1979) Die organismischen Grundlagen der geschlechtsspezifischen sportlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit. Med Sport 19: 194–205
Johnson RH, Walton JL, Krebs HA, Williamson DH (1969) Metabolic fuels during and after severe exercise in athletes and non-athletes. Lancet II: 452–455
Kindermann W, Keul J (1977) Anaerobe Energiebereitstellung im Hochleistungssport. Hoffmann-Verlag, Schorndorf
Knochel JP, Barcenas C, Cotton JR, Fuller TJ, Haller R, Carter NW (1978) Hypophosphatemia and Rhabdomyolysis. J Clin Invest 62: 1240–1246
Komi PV, Rusko H, Vos J, Vihko V (1977) Anaerobic performance capacity in athletes. Acta Physiol Scand 100: 107–114
Liesen PH (1977) Metabolische Adaptionen an akute und chronische Ausdauerbeanspruchungen. Habilitationsschrift, Deutsche Sporthochschule, Köln
Lorenz R, Gerber G (1979) Harnstoff bei körperlichen Belastungen: VerÄnderungen der Synthese, der Blutkonzentration und der Ausscheidung. Med Sport 19: 240–248
Mader A, Hollmann W (1977) Zur Bedeutung der StoffwechselleistungsfÄhigkeit des Eliteruderers im Training und Wettkampf. Beiheft zu Leistungssport 9: 8–62
Méan P, von NiederhÄusern F (1966) La femme et le sport. Gynaecologia 161: 125–150
Scheele K, Herzog W, Ritthaler G, Wirth A, Weicker H (1979) Metabolic adaptation to prolonged exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 41: 101–108
Scheibe J, Israel S, Buhl H, Köhler E (1979) Der Einflu\ extremer AusdauerlÄufe auf einzelne Organsysteme und Schlu\folgerungen für die sportmedizinische Tauglichkeitsuntersuchung. Med Sport 19: 137–140
Scheibe J, Israel S, Keil E (1980) Physiologische Reaktionen der Frau auf eine extreme Ausdauerbelastung. Med Sport 20: 19–22
Seliger V (1977) Frau und Sport. In: Hollmann W (Hrsg) Zentrale Themen der Sportmedizin, 2. Aufl. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, S 232–250
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haralambie, G., Senser, L. & Sierra-Chàvez, R. Physiological and metabolic effects of a 25 km race in female athletes. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 47, 123–131 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421664
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421664