Summary
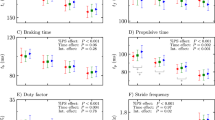
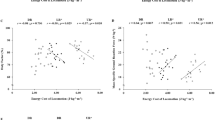
Previous studies have examined man's ability to produce external power output during maximal repetitive work cycles of short duration. It appears, however, that there were methodological limitations which would inherently mask man's true capacities. Consequently, we examined the effect of variable external loads upon external power output as measured by running upstairs. Fourteen male subjects (16–31 years of age) who regularly participated in competitive sports performed maximal stair step tests under five experimental loading conditions (no external load, 10.1, 19.2, 24.2, and 29.2kg). Significant increases (P<0.05) in external power output were found. External power output increased from a mean of 15.9 W·kg−1±1.0 (unloaded condition) to 18.5 W·kg−1±1.5 (external load of 29.2 kg). This is the first modern investigation demonstrating that external loads effect external power output as measured by this technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrand PO, Saltin B (1961) Maximal oxygen uptake and heart rate in various types of muscular activity. J Appl Physiol 16: 977–981
Blix M (1901) To the question of human working power. University Programme, Lund
Davies CTM (1971) Human power output in exercise of short duration in relation to body size and composition. Ergonomics 14: 245–256
DiPrampero PE, Pineza-Limas F, Sassi G (1970) Maximal muscular power, aerobic and anaerobic, in 116 athletes performing at the XIX Olympic Games in Mexico. Ergonomics 13: 665–674
Diaz FJ, Hagan RD, Wright JE, Horvath SM (1978) Maximal and submaximal exercise in different positions. Med Sci Sports 10: 214–217
Fox EL, Bartels RL, Klinzing J, Ragg K (1977) Metabolic responses to interval training programs of high and low power output. Med Sci Sports 9: 191–196
Hamley EJ, Thomas V (1967) Physiological and postural factors in the calibration of the bicycle ergometer. J Physiol (Lond) 191: 55P-57P
Harrison JY (1970) Maximizing human power output by suitable selection of motion cycle and load. Hum Factors 12: 315–329
Henderson SC, Ellis RW, Klimovitch G, Brooks GA (1977) The effects of circular and elliptical chainwheels on steady-rate cycle ergometer work efficiency. Med Sci Sports 9: 202–207
Houston ME, Thomson JA (1977) The response of endurance-adapted adults to intense anaerobic training. Eur J Appl Physiol 36: 207–213
Kasch FW, Wallace JP, Huhn RR, Krogh LA, Hurls PM (1976) VO2 max during horizontal and inclined treadmill running. J Appl Physiol 40: 982–983
Komi PV, Rusko H, Vos J, Vihko V (1977) Anaerobic performance capacity in athletes. Acta Physiol Scand 100: 107–114
Komi PV, Karlsson J (1978) Skeletal muscle fiber types, enzyme activities, and physical performance in young males and females. Acta Physiol Scand 103: 210–218
Margaria R, Aghemo P, Rovelli E (1966) Measurement of muscular power (anaerobic) in man. J Appl Physiol 21: 1662–1664
Margaria R, DiPrampero PE, Aghemo P, Derevenco P, Mariani M (1971) Effect of steady-state exercise on maximal anaerobic power in man. J Appl Physiol 30: 885–889
McKay GA, Banister EW (1976) A comparison of maximal oxygen uptake determination by bicycle ergometry at various pedalling frequencies and by treadmill running at various speeds. Eur J Appl Physiol 35: 191–200
Milliken MP, Spence DW (1973) Measurement of power in athletes. Coach and Athlete 30: 12–14
Runyan RP, Huber A (1971) Fundamentals of Behavioral statistics. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, pp 223–224
Schennum PL, deVries HA (1976) The effect of saddle height on oxygen consumption during bicycle ergometer work. Med Sci Sports 8: 119–121
Taylor HL, Buskirk E, Henschel A (1955) Maximal oxygen intake as an objective measure of cardio-respiratory performance. J Appl Physiol 8: 73–80
Thorstensson A, Sjodin B, Karlsson J (1975) Enzyme activities and muscle strength after “sprint training” in man. Acta Physiol Scand 94: 313–318
Vihko V, Soimajarvi J, Karvinen E, Rahkila P, Havu M (1978) Lipid metabolism during exercise I: Physiological and biochemical characterization of normal healthy male subjects in relation to their physical fitness. Eur J Appl Physiol 39: 209–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caiozzo, V.J., Kyle, C.R. The effect of external loading upon power output in stair climbing. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 44, 217–222 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421620
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421620