Summary
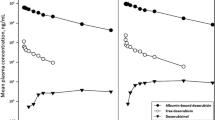
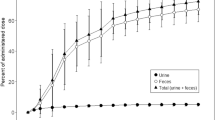
Bleomycin pharmacokinetics were studied by radioimmunoassay in 11 patients who received 7–30 U intravenously (IV) and eight patients who received 4–30 U subcutaneously (SC). For patients who received IV bleomycin plasma disappearance was biphasic, with a mean initial half-life of 0.26 h and a terminal half-life of 2.3 h. Mean plasma drug clearance was 67.8 ml/min/m2 and the volume of distribution was 13.2 l/m2. Urinary excretion accounted for 63.9% of the drug in 24 h. After SC administration peak plasma levels occurred in 1.1 h, with a mean elimination half-life of 4.3 h. Mean plasma drug clearance was 60.5 ml/min/m2 and the volume of distribution was 19.2 l/m2. Bleomycin plasma clearance correlated well with serum creatinine (r2=0.72).
Bleomycin has a rapid plasma elimination and urinary excretion. Bleomycin bioavailability after SC administration appears comparable to that seen after IV administration as determined by the areas under the plasma disappearance curves. Prolonged plasma levels are seen after SC injection, suggesting this route of administration can produce plasma concentrations comparable to those attained with continuous IV infusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts D, Hsiao-Sheng C, Liu R, Chen J, Mayershon M, Perrier D, Moon T, Gross J (1978) Systemic absorption of bleomycin after intracavitary administration. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 19: 77
Broughton A, Strong JE (1976) Radioimmunoassay of bleomycin. Cancer Res 35: 1418–1421
Crooke ST, Comis RL, Einhorn LH, Strong JE, Broughton A, Prestayko AW (1977a) Effects of variation in renal function on the clinical pharmacology of bleomycin administered as an IV bolus. Cancer Treat Rep 61: 1631–1636
Crooke ST, Luft FT, Broughton AW, Strong JE, Casson K, Einhorn L (1977b) Bleomycin serum concentrations in a patient with varying renal function. Cancer 39: 1430–1434
Fujita H, Kimura K (1970) Blood levels, tissue distribution, excretion and inactivation of bleomycin. In: Progress in antimicrobial and anticancer chemotherapy. Proc 6th Intern Cong Chemother, vol 2. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 309–314
Kramer WG, Feldman S, Broughton A, Strong JE, Hall SW, Holoye PY (1978) The pharmacokinetics of bleomycin in man. J Clin Pharmacol 18: 346–352
Ohnuma T, Holland JF, Masuda H, Waligunda JA, Goldberg GA (1974) Microbiologic assay of bleomycin: Inactivation, tissue distribution and clearance. Cancer 33: 1230–1238
Pittillo RF, Wolley C, Rice LS (1971) Bleomycin, an antitumor antibiotic-improved microbiological assay and tissue distribution studies in normal mice. Appl Microbiol 22: 564–566
Strong JE, Broughton A, Crooke ST (1977) Specificity of antiserum produced against bleomycin. Cancer Treat Rep 61: 1509–1512
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hall, S.W., Strong, J.E., Broughton, A. et al. Bleomycin clinical pharmacology by radioimmunoassay. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 9, 22–25 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296756
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296756