Summary
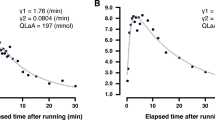
The effects of physical conditioning on plasma fibrinolytic activity were studied in two groups of subjects. Volunteers not engaged in any sport were compared with individuals having been subjected to aerobic conditioning (middle-distance runners, defined as men running more than 80 km per week). Plasma concentrations of the different components of the fibrinolytic system were evaluated before and immediately after a maximal effort treadmill protocol. Comparison of the resting parameters revealed that under basal conditions for plasma concentrations of plasminogen, fibrinogen, α2-antiplasmin, protein C and protein S there were no differences between the two groups. Concentrations of the fibrin degradation products (FbDP) and fibrinogen degradation products (FgDP) were significantly higher in the runners than in the control group, indicating an increased fibrinolytic potential that seemed to be a consequence of the reduced formation of tissue plasminogen activator-plasminogen activator inhibitor (t-PA-PAI) complexes. Acute maximal exercise resulted in pronounced fibrinolysis, evidenced by the elevation of FbDP and FgDP concentrations, in both groups of subjects. The acceleration of the fibrinolytic activity was larger in conditioned individuals, which could be accounted for by a higher t-PA release and reduced formation of t-PA-PAI complexes when compared to the untrained subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abilgaard U (1977) Antithrombin (heparin cofactor) assay with new chromogenic substrates. Thromb Res 11:549–553
Amiral J, Plassart V, Grosley M, Mimilla F, Contant G, Guyader AM (1988) Measurement of t-PA-PAI-1 complexes by ELISA using monoclonal antibodies: clinical relevance. Thromb Res [Suppl VIII]:99–113
Arai M, Yorifuji H, Ikematsu S, Nagasawa H, Fujimaki M, Fukutake K, Katsumura K, Ishii T, Iwane H (1990) Influence of strenous exercise (triathlon) on blood coagulation and fibrinolytic system. Thromb Res 57:465–471
Bourey RE, Santoro SA (1988) Interactions of exercise, coagulation, platelets and fibrinolysis — a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 20:439–446
Bruce R (1972) Multi-stage treadmill test of submaximal and maximal exercise. In: Committee on Exercise, American Heart Association (ed) Exercise testing and training of apparently healthy individuals: a handbook for physicians. American Heart Association, Dallas, Tex, pp 32–34
Carter JEL, Yuhasz MS (1984) Skinfolds and body composition of olympic athletes. Med Sport Sci 18:114–182
Chmielevska J, Wiman B (1986) Determination of tissue plasminogen activator and its “fast” inhibitor in plasma. Clin Chem 32:482–485
Clauss A (1957) Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Hematol 17:237–239
Colwell JA (1986) Effects of exercise on platelet function, coagulation, and fibrinolysis. Diabetes Metab Rev 4:501–512
Comp PC, Doray D, Patton D, Esmont C (1986) An abnormal plasma distribution of protein S occurs in functional protein S deficiency. Blood 67:504–508
D'Angelo A, Lockhart MS, D'Angelo SV, Taylor FB (1987) Protein S is a cofactor for activated protein C neutralization of an inhibitor of plasminogen activation released from platelets. Blood 69:231–237
Davis GL, Abilgaard CF, Bernauer CH (1976) Fibrinolysis and hemostatic changes during and after maximal exercise in males. J Appl Physiol 40:287–292
Dooijewaard G, De Boer A, Turion PN, Cohen AF, Breimer DD, Kluft C (1991) Physical exercise induces enhancement of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PA) levels in plasma. Thromb Haemost 65:82–86
Drygas WK (1988) Changes in blood platelet function, coagulation, and fibrinolytic activity in response to moderate, exhaustive and prolonged exercise. Int J Sports Med 9:67–72
Dufaux B, Order U, Hollmann W (1984) Can physical exercise induce an effective fibrinolysis? Thromb Res 36:37–43
Ferguson EW, Guest MM (1974) Exercise, physical conditioning, blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Thromb Diasth Haemorrh 31:63–71
Ferguson EW, Bernier LL, Banta GR, Yu-Yahiro J, Schoomaker EB (1987) Effects of exercise and conditioning on clotting and fibrinolytic activity in men. J Appl Physiol 62:1416–1421
Goldberg L, Elliot DL (1987) The effect of exercise on lipid metabolism in men and women. Sports Med 4:307–321
Graef H, Hafter R (1982) Detection and relevance of crosslinked fibrin derivatives in blood. Semin Thromb Hemost 8:57–68
Hamsten H, Wiman B, De Faire U, Blomback M (1985) Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Eng J Med 313:1557–1563
Hansen JB, Wilsgard L, Olsen JO, Osterud B (1990) Formation and persistence of procoagulant and fibrinolytic activities in circulation after strenous physical exercise. Thromb Haemost 64:385–389
Huisveld IA, Hospers AJH, Bernink MJE, Biersteker MWA, Erich WBM, Bouma BN (1982) Oral contraceptives and fibrinolysis among female cyclists before and after exercise. J Appl Physiol 53:330–334
Huisveld IA, Kluft C, Hospers AJH, Bernink MJE, Erich WBM, Bouma BN (1984) Effect of exercise and oral contraceptive agents on fibrinolytic potential in trained females. J Appl Physiol 56:906–913
Jones NL (1988) Clinical exercise testing. Saunders, Philadelphia
Knot EAR, Porte RJ, Terpstra OT, Schalm SW, Willemse PJ, Groenland THN, Stibbe J, Dooijewaard G, Nieuwenhuizen W (1988) Coagulation and fibrinolysis in the first human auxiliary partial liver transplantation in Rotterdam. Fibrinolysis 2:111–117
Koppert PW, Kuipers W, Hoegee-de Nobel E, Brommer EJP, Koopman J, Nieuwnhuizen W (1987) A quantitative immunoassay for primary fibrinogenolysis products in plasma. Thromb Haemost 57:25–28
Koppert PW, Hoegee-de Nobel E, Nieuwenhuizer W (1988) A monoclonal antibody-based enzyme immunoassay for fibrin degradation products in plasma. Thromb Haemost 59:310–315
Korninger C, Wagner O, Binder BR (1985) Tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor in human plasma: development of a functional assay system and demonstration of a correlating Mr=50000 antiactivator. J Lab Clin Med 105:718–724
Korninger C, Speiser W, Wotja J, Binder BR (1986) Sandwich ELISA for t-PA antigen employing a monoclonal antibody. Thromb Res 41:527–535
Korninger C, Jager R, Huber K, Lechner K (1988) Levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor in patients with angina pectoris. Klin Wochenschr 66:59–61
Lokey EA, Tran ZV (1989) Effects of exercise training on serum lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in women: a meta-analysis. Int J Sports Med 10:424–429
Mandalaki T, Desypris A, Louzou C, Poulou CP, Dimitriadou C (1980) Marathon run. III: Effects on coagulation, fibrinolysis, platelet coagulation and serum cortisol levels. Thromb Haemost 43:49–51
Marder VJ, Budzynski AZ (1975) Data for defining fibrinogen and its plasmic degradation products. Thromb Diasth Haemorrh 33:197–202
Martinoli JL, Stocker K (1986) Fast functional protein C assay using Protac, a novel protein C activator. Thromb Res 43:253–264
Mehta J, Lawson D, Saldeen TJ (1988) Reduction in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) with omega-3polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) intake. Am Heart J 116:1201–1206
Paramo JA, Colucci M, Collen D, Van de Werf F (1985) Plasminogen activator inhibitor in the blood of patients with coronary artery disease. BMJ 291:573–574
Preissner KT (1990) Biological relevance of the protein C system and laboratory diagnosis of protein C and protein S deficiencies. Clin Sci 78:351–364
Prowse CV, Cash JD (1984) Physiologic and pharmacologic enhancement of fibrinolysis. Semin Thromb Hemost 10:51–60
Röcker L, Taenzer M, Drygas WK, Lill H, Heyduck B, Altenkirch HU (1990) Effect of prolonged physical exercise on the fibrinolytic system. Eur J Appl Physiol 60:478–481
Samama M (1990) Physiologie et exploration de l'hemostase. Doin, Paris
Sinzinger H, Virgolini I (1988) Effects of exercise on parameters of blood coagulation, platelet function and the prostaglandin system. Sports Med 6:238–245
Soria J, Soria C, Samama MA (1986) A plasminogen assay using a chromogenic synthetic substrate. Results for clinical work and studies of thrombosis. In: Davidson J (ed) Progress in chemical fibrinolysis and thrombolysis. Churchill Livingstone, London, pp 337–346
Speiser W, Langer W, Pschaick A, Selmayr E, Ibe B, Nowacki PE, Muller-Berghaus G (1988) Increased blood fibrinolytic activity after physical exercise: comparative study in individuals with different sporting activities and in patients after myocardial infarction taking part in a rehabilitation sport program. Thromb Res 51:543–555
Stratton JR, Chandler WL, Schwartz RS, Cerqueira MD, Levy WC, Kahn SE, Larson VG, Cain KC, Berad JC, Abrass IB (1991) Effects of physical conditioning on fibrinolytic variables and fibrinogen in young and old healthy adults. Circulation 83:1692–1697
Teger-Nilsson AC, Friberger P, Gyzander E (1977) Determination of a new rapid plasmin inhibitor in human blood by means of a plasmin specific tripeptide substrate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 73:403–409
Van Beaumont W (1972) Evaluation of hemoconcentration from hematocrit measurements. J Appl Physiol 32:712–713
Van Beaumont W, Underkofler S, Van Beaumont S (1981) Erythrocite volume, plasma volume, and acid-base changes in exercise and heat dehydration. J Appl Physiol 50:1255–1262
Van Hinsberg VWM, Bentina RM, Van Vyngaarden A, Van Tilburg NH, Emeis JJ, Haverkate F (1985) Activated protein C decreases plasminogen activator-inhibitor activity in endothelial cell-conditioned medium. Blood 65:444–451
Wasserman K, Whipp BJ, Koyal SN, Beaver BL (1973) Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol 35:236–243
Wheeler ME, Davis GL, Gillespie WJ, Bern MM (1986) Physiological changes in hemostasis associated with acute exercise. J Appl Physiol 60:986–990
Williams RS, Eden S, Andersen J (1981) Reduced epinephrineinduced platelet aggregation following cardiac rehabilitation. J Clin Res 11:127–134
Wiman B, Jungberg B, Chmielevska J, Urden G, Blomback M, Johnson H (1985) The role of the fibrinolytic system in deep venous thrombosis. J Lab Clin Med 105:265–270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Paz, J.A., Lasierra, J., Villa, J.G. et al. Changes in the fibrinolytic system associated with physical conditioning. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 65, 388–393 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00243502
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00243502