Abstract
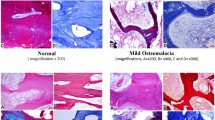
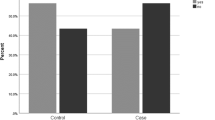
Skeletal fluorosis continues to be endemic in many parts of India. Osteosclerosis and interosseous membrane calcification have long been regarded as hallmarks of this disease. Our study showed in addition a wide variety of radiological patterns: coarse trabecular pattern, axial osteosclerosis with distal osteopenia and diffuse osteopenia. Subjects with osteopenic changes had a significantly lower dietary intake of calcium than those groups having normal radiological findings, predominant osteosclerosis or coarse trabecular pattern (p<0.001, p<0.01, and p<0.01 respectively). This suggests the role of calcium intake in determining the skeletal changes in endemic fluorosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boivin G, Meunier PJ (1990) Fluoride and bone: toxicological and therapeutic aspects. In: Cohen RD, Lewis B, Alberti KGMM, Denman AM (eds) The metabolic and molecular basis of acquired disease. Baillière Tindall, London, p 1803
Boivin G, Chavassieux P, Chapuy MC, Baud CA, Meunier PJ (1986) Profil histomorphometrique de la fluorose osseuse induite par l'ingestion prolongée d'eau de Vichy Saint-Yorre. Comparaison avec le taux de fluor osseux. Pathol Biol (Paris) 34:33
Christie DP (1980) The spectrum of radiological bone changes in children with fluorosis. Radiology 136:85
Dandona P, Menon RK, Shenoy R, Houlder S, Thomas M, Mallinson WJW (1976) Low 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and normal osteocalcin in elderly subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 63:459
Griffiths HJ, Hunt RD, Zimmerman RE, Finberg H, Cuttino J (1975) The role of calcium and fluoride in osteoporosis in Rhesus monkeys. Invest Radiol 10:263
Gruber HE, Baylink DJ (1991) The effects of fluoride on bone. Clin Orthop Rel Res 267:264–277
Jackson WPU (1962) Further observations on Kenhardt bone disease and its relation to fluorosis. S Afr Med J 36:932
Jolly SS, Singh BM, Mathur OC (1969) Endemic fluorosis in Punjab (India). Am J Med 47:553
Krishnamachari KAVR (1976) Further observations in syndrome of endemic genu valgum. Ind J Med Res 64:284
Krishnamachari KAVR, Krishnaswamy K (1973) Genu valgum and osteoporosis in an area of endemic fluorosis. Lancet 2:887
Manzke E, Rawley R, Vose G, Roginsky M, Rader JI, Baylink DJ (1977) Effect of fluoride therapy on nondialyzable urinary hydroxyproline, serum alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone, and 25 hydroxyvitamin D. Metabolism 26:1005
Reddy SG, Rao NBS (1971) Effect of dietary calcium, vitamin C and protein in development of experimental skeletal fluorosis. II. Calcium turnover with 45Ca; calcium and phosphorus balances. Metabolism 20:650
Siddique AH (1955) Fluorosis in Nalgonda district, Hyderabad, Deccan. Br Med J 2:1408
Teotia SPS, Teotia M (1973) Secondary hyperparathyroidism in endemic fluorosis. Br Med J 1:637
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mithal, A., Trivedi, N., Gupta, S.K. et al. Radiological spectrum of endemic fluorosis: relationship with calcium intake. Skeletal Radiol. 22, 257–261 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197670
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197670