Abstract
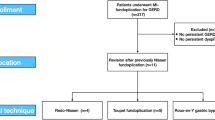
Nineteen patients underwent laparoscopic reoperations for failed or complicated antireflux operations from a total of 248 patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease who had been operated on by this approach. Sixteen had been submitted to open surgery and three to laparoscopic surgery over a period ranging from 5 days to 31 years before the study. Three patients had been submitted to two open antireflux surgeries previously. Seventeen patients had recurrent reflux esophagitis after different types of surgeries, and two patients presented with gastric strangulation after fundoplication. The causes of recurrence were: slipped total fundoplications (3), disruption of total and partial fundoplications (6), too-tight total fundoplication (1), too-low (gastric) partial fundoplication (1), Allison procedure (1), partial fundoplication and paraesophageal hernia (2), and unknown (3). The laparoscopic approach was used in 18 patients and a laparoscopic-thoracoscopic approach in 1. The procedures included laparoscopic total fundoplications (11), partial fundoplications (4), transhiatal esophagectomy (1), Collis-Nissen (1), Roux-en-Y gastrectomy and thoracoscopic vagotomy (1), and intrathoracic fundoplication (1). One patient was converted to open surgery. Intraoperative complications included 1 pneumothorax, 1 gastric perforation, and 1 esophageal perforation during the introduction of a Maloney dilator. Mean operative time was 210 min, ranging from 140 to 320 min. Mean hospital stay was 3.1 days after treatment of failed operations and 22 days after treatment of complications. Postoperative complications included subcutaneous infection (1), gastric fistula (1), and liver hematoma (1). The results have been excellent and good in 84.3% of the patients after a mean follow-up of 13 months. We concluded that laparoscopic reoperations are technically feasible with good preliminary results provided that the mandatory expertise is available.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collard JM, De Koninck XJ, Otte JB, Fiasse RHMD, Kestens PJ (1991) Intrathoracic Nissen fundoplication: long-term clinical and pH monitoring evaluation. Ann Thorac Surg 51: 34–38
Cushieri A (1992) Laparoscopic reduction, crural repair and fundoplication of large hiatal hernia. Am J Surg 163: 420–430
Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C (1991) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc 1: 138–143
De Meester TR, Bonaviva L, Albertucci M (1986) Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg 204: 9
De Paula AL, Hashiba K, Ferreria EAB, Paula RA, Grecco E (1995) Laparoscopic transhiatal esophagectomy with esophagogastroplasty. Surg Laparosc Endosc 5: 1–5
Fekete F, Pateron D (1981) What is the place of antrectomy with Roux-en-Y in the treatment of reflux disease? Experience with 83 total duodenal diversions. World J Surg 16: 349–353
Leonardi HK, Crozier RE, Ellis Jr H (1981) Reoperation for complications of the Nissen fundoplication. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 81: 50–56
Little AG, Ferguson MK, Skinner DB (1986) Reoperation for failed antireflux operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 91: 511–517
Low DE, Mercer CD, James EE, Hill LD (1988) Post-Nissen syndrome. Surg Gynecol Obstet 167: 1–5
Luostarinen ME, Isolauri JO, Koskinen MO, Laitinen JO, Matikainen MJ, Lindholm S (1993) Refundoplication for recurrent gastroesophageal reflux. World J Surg 17: 587–594
Negre JB (1983) Post-fundoplication symptoms: do they restrict the success of Nissen fundoplication? Ann Surg 198: 698–700
Richardson JD, Larson GM, Polk Jr HC (1982) Intrathoracic fundoplication for shortened esophagus. Treacherous solution to a challenging problem. Am J Surg 143: 29–35
Siewert JR, Isolarui J, Feussner H (1989) Reoperation following failed fundoplication. World J Surg 13: 791–797
Skinner D (1992) Surgical management after failed antireflux operations. World J Surg 16: 359–363
Stirling MC, Orringer MB (1986) Surgical treatment after the failed antireflux operation. J Thorac Cardio Surg 92: 667–672
Weerts JM, Dallemagne B, Hamoir E, Demarche M, Markiewicz S, Jehaes C, Lombard R, Demoulin JC, Etienne M, Ferron PE, Fontaine F, Gillard V, Delforge M (1993) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: detailed analysis of 132 patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc 3: 357–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DePaula, A.L., Hashiba, K., Bafutto, M. et al. Laparoscopic reoperations after failed and complicated antireflux operations. Surg Endosc 9, 681–686 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00187939
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00187939