Summary
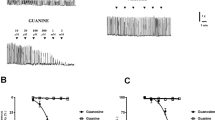
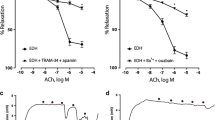
Ouabain (10−7 to 10−4 M) elicited concentration-dependent contractile responses in human placental arteries. The contractions were reduced by 10−4 M amiloride and Ca2+-free medium, but not affected by 10−6 M nifedipine or 10−6 M Bay-K-8644, which markedly reduced or potentiated 75 mM K+-induced contractions, respectively. After contracting the vessels with 10−6 M prostaglandin F2α in a K+-free medium, the subsequent addition of 7.5 mM K+ induced a marked relaxation, which was blocked by 10−6 M ouabain. This glycoside (10−8 to 10−4 M) also produced a concentration-dependent reduction of 86Rb+ uptake. Scatchard analysis of the [3H]-ouabain binding to membrane fractions from human placental arteries suggests a single class of binding sites with a KD of 88.3 nM and a Bmax of 345 fmol/mg. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT; 10−9 to 10−5 M) caused concentration-dependent contractions. Single concentrations produced transient responses composed of an initial contraction, followed by a slow fall in tension. Ouabain (10−8 to 10−6 M), K+-free medium or the reduction of bath temperature (28°C) did not modify contractions but inhibited the relaxant phase of the response. 5-HT (10−8 to 10−6 M) increased both total and ouabain-insensitive 86Rb+ uptake, but the difference between them was not modified. These data indicate that: (1) human placental arteries possess an important sodium pump activity, inhibition or stimulation of which markedly alters vascular tone, (2) ouabain-evoked contractions are produced by Ca2+ entry mainly through Na+-Ca2+ exchange, secondary to intracellular Na+ accumulation, (3) the relaxant component of 5-HT response is dependent on the activity of the sodium pump, (4) the activation of Na+,K+-ATPase activity by this amine is not apparently due to direct effect, and (5) the inhibition of the sodium pump can cause long lasting increases of placental vascular resistance in the presence of physiological concentrations of 5-HT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarhus LL, Shepherd JT, Tyce GM, Verbeuren TJ, Vanhoutte PM (1983) Contractions of canine vascular smooth muscle cells caused by ouabain are due to release of norepinephrine from adrenergic nerve endings. Circ Res 52:501–507
Adams RJ, Wallick ET, Asano E, Disalvo J, Fondacaro JD, Jacobson ED (1983) Canine mesenteric artery Na+,K+-ATPase: vasopressor receptor for digitalis? J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 5:468–482
Allen JC, Navran SS (1984) Role of the Na+ pump in smooth muscle contractile regulation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 5:462–465
Altschuld RA, Hohl GM, Lamka KK, Brierley GP (1984) Effects of amiloride on calcium uptake by myocytes isolated from adult rat hearts. Life Sci 35:865–870
Altura BM, Malaviya D, Reich CF, Orkin LD (1972) Effects of vasoactive agents in isolated human umbilical arteries and veins. Am J Physiol 222:345–355
Bell DR, Babcock CH, Bohr DF (1989) Individualities in post-serotonin attenuation and Na+/K+ pump activity in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 171:189–199
Bhargava I, Raja PTK (1970) An anatomical study of foetal blood vessels on the chorial surface of the human placenta. Acta Anat 75:13–26
Blaustein MP (1977) Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis. Am J Physiol 232:C165-C173
Bolton TB (1979) Mechanisms of action of transmitter and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev 59:606–718
Bonaccorsi A, Hermsmeyer K, Smith CB, Bohr DF (1977) Norepinephrine release in isolated arteries induced by K-free solution. Am J Physiol 232:H140-H145
Bova S, Cargnelli G, Luciani S (1988) Na/Ca exchange and tension development in vascular smooth muscle: effect of amiloride. Br J Pharmacol 93:601–608
Briggs AM, Shibata S (1966) Ca and ouabain interaction on vascular smooth muscle. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 121:274–278
Bukoski RD, Seidel CL, Allen JC (1983) Ouabain binding Na+,K+-ATPase activity, and 86Rb uptake of canine arteries. Am J Physiol 245:H604-H609
Charnock JS, Doty DM, Russell JC (1971) The effect of temperature on the activity of Na, K-ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys 142:633–637
Chaterjee M, Chin PSJ, Doll RJ, Sybertz EJ (1988) Effect of amiloride on regulatory mechanisms of vascular smooth muscle contraction. Biochem Pharmacol 37:813–818
De Wardener HE, Millet J, Holland S, MacGregor GA, Alaghband J (1987) Ouabainlike Na,K-ATPase inhibitor in the plasma of normotensive and hypertensive humans and rats. Hypertension 10:152–157
Debetto P, Floreani M, Carpenedo F, Luciani S (1987) Inhibition of the Na+/Ca2+ exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles by amiloride. Life Sci 40:1523 -1530
Delva P, Capra C, Degan M, Minuz D, Covi G, Milan L, Steele A, Lechi A (1989) High plasma levels of a ouabain-like factor in normal pregnancy and in preeclampsia. Eur J Clin Invest 19:95–100
Deth RC, Lynch CJ (1980) The binding of 3H-ouabain to Na+-K+-ATPase sites arterial smooth muscle. Pharmacology 21:29–37
Diemer HP, Hemming BA, Kaumann AJ (1985) Two classes of 5-HT-receptors in umbilical arteries of man. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 330:R65
Ebara H, Suzuki S, Nagashima K, Koizumi A, Kanbey Y, Kuroume T (1986) Digoxin and digoxin-like immunoreactive substances in amniotic fluid, cord blood and serum of neonates. Pediatr Res 20:28–31
Fleming WW (1980) The electrogenic Na+,K+-pump in smooth muscle: physiologic and pharmacologic significance. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:129–149
Fox AAI, Borchard U, Newmann M (1983) Effects of vanadate on isolated vascular tissue: biochemical and functional investigations. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 5:309–316
Gerthoffer WT, Allen JC (1981) Characteristics of binding of [3H]-ouabain to smooth muscle sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase and quantitation of sodium-potassium pump sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 217:692–696
Graves SW (1987) The possible role of digitalislike factors in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Hypertension 10:I84-I86
Haddy FJ (1983) Potassium effects on contraction in arterial smooth muscle mediated by Na+,K+-ATPase. Fed Proc 42:239–245
Hamlyn JM, Ringel R, Schaeffer J, Levinson PD, Hamilton BP, Kowarki AA, Blaustein MP (1982) A circulating inhibitor of Na,K-ATPase, associated with essential hypertension. Nature 300:650–652
Hayashi S, Park MK (1984) Neurogenic and myogenic contractile responses of dog mesenteric arteries to reduced K+ concentration and their interactions with ouabain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:527–533
Hendrickx H, Casteels R (1974) Electrogenic sodium pump in arterial smooth muscle cells. Pflügers Arch 346:299–306
Hermsmeyer K (1983) Sodium pump hyperpolarization-relaxation in rat caudal artery. Fed Proc 42:246–252
Hernández RJ (1982) A serotonin agonist-antagonist reversible effect of Na,K-ATPase activity in the developing rat brain. Dev Neurosci 5:326–331
Hernández RJ (1987) Brain Na, K-ATP activity possibly regulated by a specific serotonin receptor. Brain Res 408:399–402
Honerjager P (1982) Cardioactive substances that prolong the open state of sodium channels. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 92:1–74
Jones JB, Rowsell A (1973) Fetal 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in late pregnancy. J Obst Gynecol 80:687–689
Karaki H, Ozaki H, Urakawa N (1978) Effects of ouabain and potassium-free solution on the contractions of isolated blood vessels. Eur J Pharmacol 48:439–443
Kelly JG, Naidu RK, Molley KD (1981) Evidence for a circulating sodium transport inhibitor in essential hypertension. Br Med J 282:1241
Køren Z, Pfeifer Y, Sulman FG (1965) Serotonin content of human placenta and fetus during pregnancy. Am J Obst Gynecol 93:411–415
Krampetz IK, Bose R (1988) Relaxant effect of amiloride on canine tracheal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:641–648
Lang S, Blaustein MP (1980) The role of the sodium pump in the control of vascular tone in the rat. Circ Res 46:463–470
Logan CJ, O'Donovan JD (1976) The effects of ouabain and the activation of neural membrane ATPase by biogenic amines. J Neurochem 27:185–189
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randell RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maigaard S, Forman A, Andersson KE (1985) Digoxin inhibition of relaxation induced by prostacyclin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in small human placental arteries. Placenta 6:435–443
Maigaard S, Forman A, Andersson KE (1986) Relaxant and contractile effects of some amines and prostanoids in myometrial and vascular smooth muscle within the human uteroplacental unit. Acta Physiol Scand 128:33–40
Mak KKW, Gude NM, Walters WAW, Boura ALA (1984) Effects of vasoactive autacoids on the human umbilical-placental placental vasculature. Br J Obst Gynecol 91:99–106
Marín J (1989) Vascular effects of calcium antagonists. Uses in some cerebrovascular disorders. Gen Pharmacol 19:295–306
Marín J, Sánchez-Ferrer CF, Salaices M (1988) Effects of ouabain on isolated cerebral and femoral arteries of the cat: a functional and biochemical study. Br J Pharmacol 93:43–52
Montenegro R, Knuppel RA, Shah D, O'Brien WF (1985) The effect of serotonin blockade in postpartum preeclamptic patients. Am J Obst Gynecol 153:130–134
Moreland RS, Van Breemen C, Bohr DF (1985) Mechanism by which serotonin attenuates contractile response of canine mesenteric arterial smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:322–329
Navran SS, Allain G, García HF, Allen JC, Seidel CL (1991) Serotonin-induced Na+/K+ pump stimulation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for coupling to multiple receptor mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:297–303
Navran SS, Allen JC (1986) Comparison of ouabain-sensitive 86Rb uptake of canine and femoral arteries. Am J Physiol 251:C247-C251
O'Reilly S, Loncin M (1967) Ceruloplasmin and 5-hydroxyindole metabolism in pregnancy. Am J Obst Gynecol 97:8–12
Odendaal HJ, Beyers AD, Van Heyningen CF, Spruyt LL, Kotze TJVW, Van Jaarsveld PP (1986) Immunoreactive digitalislike substance in preeclampsia. S Afr Med J 70:535–537
Overbeck HW (1987) The vascular Na,K-pump in experimental hypertension. Hypertension 10:I95-I100
Ozaki H, Karaki H, Urakawa N (1978) Possible role of Na-Ca exchange mechanism in contractions induced in guinea-pig aorta by potassium-free solution and ouabain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 304:203–209
Ozaki H, Urakawa N (1979) Na-Ca exchange and tension development in guinea-pig aorta. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 309:171–178
Palaty V (1980) The transient contractile response of the isolated rat tail artery to inhibition of the sodium pump. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 58:336–339
Reviriego J, Fernández-Alfonso MS, Marín J (1990) Actions of vasoactive drugs on human placental vascular smooth muscle. Gen Pharmacol 21:719–727
Reviriego J, Marín J (1989) Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on human isolated placental chorionic arteries and veins. Br J Pharmacol 96:961–969
Sánchez-Ferrer CF, Marín J, Valverde A, Salaices M (1988) Actions of vanadate on vascular tension and sodium pump activity in cat isolated cerebral and femoral arteries. Br J Pharmacol 93:53–60
Sato K, Aoki K (1988) Biphasic contraction induced by ouabain in human umbilical arteries. Eur J Pharmacol 158:299–302
Sharma RV, Bendhack RV, Bhalla RC (1988) Mechanism of inhibition of rat caudal artery contraction by amiloride. J Cardiovase Pharmacol 12:152–159
Toda N (1980)Mechanisms of ouabain-induced arterial muscle contractions. Am J Physiol 239:H199-H205
Tulenko TN (1979) Regional sensitivity to vasoactive polypeptides in the human umbilicoplacental vasculature. Am J Obst Gynecol 135:629–636
Van Breemen C, Aaronson P, Loutzenhiser R (1979) Sodium-calcium interactions in mammalian smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev 30:167–208
Walker DW, McLean JR (1971) Absence of adrenergic nerves in the human placenta. Nature 229:344–345
Wallick ET, Adams RJ, Fondacaro JD, Jacobson JD (1982) Na+,K+-ATPase of the canine mesenteric artery. Fed Proc 41:2101–2105
Webb RC, Bohr DF (1978) Potassium-induced relaxation as an indicator of Na+-K+ ATPase activity in vascular smooth muscle. Blood Vessels 15:198–207
Whitsett JA, Wallick ET (1980) [3H]-ouabain binding and Na+-K+-ATPase activity in human placenta. Am J Physiol 238: E38-E45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to J. Marin at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Alfonso, M.S., Sánchez-Ferrer, C.F., Salaices, M. et al. Functional role of sodium pump in human placental arteries. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345, 108–116 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175477
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175477