Abstract
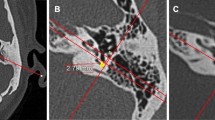
Using high-resolution computed tomography, we measured the cross-sectional area of mastoid air cells and the shortest distance between the external auditory canal and the anterior edge of the sigmoid sinus (DIST), and then compared the right-left difference in 70 patients with unilateral chronic otitis media and 23 cases without middle ear disease. DIST was significantly short where there was poor mastoid pneumatization (P < 0.0001), regardless of whether it was the right or left ear. Furthermore, on the well-pneumatized temporal bone, the increase in size of the cross-sectional area was closely correlated with the increase in DIST (r = 0.495). We suggest that the relative position of the external auditory canal and the sigmoid sinus is affected by middle ear inflammations in childhood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki K, Esaki S, Honda Y, Tos M (1990) Effect of middle ear infection on pneumatization and growth of the mastoid process. An experimental study in the pig. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 110:399–409
Graham MD (1977) The jugular bulb: its anatomic and clinical considerations in contemporary otology. Laryngoscope 87:105–125
Ichijo H, Hozawa J, Ota S, Miyano K (1989) Anatomical study of the superior jugular bulb by use of high-resolution computed tomography. J Otolaryngol Jpn 92:1934–1938
Ichijo H, Hosokawa M, Shinkawa H (1993) Differences in size and shape between the right and left sigmoid sinuses. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 250:297–299
Ikarashi H, Nakano Y (1987) The effect of chronic middle ear inflammation on the pneumatization of the tympanic bulla in pigs. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 104:130–137
Orr JB, Todd NW (1988) Jugular bulb position and shape are unrelated to temporal bone pneumatization. Laryngoscope 98: 136–138
Potter GD (1973) The ear, the surgeon and the radiologist. Am J Roentgenoll 18:501–510
Schatz A, Sadé J (1990) Correlation between mastoid pneumatization and position of the lateral sinus. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 99:142–145
Tos M (1982) Mastoid pneumatization. A critical analysis of the hereditary theory. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 94:73–80
Tos M, Stangerup S-E, Andreassen UK (1985) Size of the mastoid air cells and otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 94: 386–392
Turgut S, Tos M (1992) Correlation between temporal bone pneumatization, location of lateral sinus and length of the mastoid process. J Laryngol Otol 106:485–489
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ichijo, H., Hosokawa, m. & Shinkawa, H. The relationship between mastoid pneumatization and the position of the sigmoid sinus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 253, 421–424 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168495