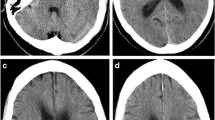
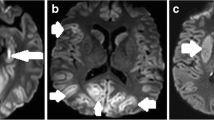
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barzo P, Marmarou A, Fatouros P, Hayasaki K, Corwin F (1997) Contribution of vasogenic and cellular edema to traumatic swelling measured by diffusion-weighted imaging. J Neurosurg 87: 900–907
Ito J, Marmarou A, Barzo P, Fatouros P, Corwin F (1996) Characterization of edema by diffusion-weighted imaging in experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 84: 97–103
Katayama Y, Tsubokawa T, Miyazaki S, Kawamata T, Yoshino A (1990) Oedema fluid formation within contused brain tissue as a cause of medically uncontrollable elevation of intracranial pressure in head trauma patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 51: 308–310
Katayama Y, Tsubokawa T, Kinoshita K, Himi K (1992) Intra parenchymal fluid-blood levels in traumatic intracerebral hematomas. Neuroradiol 34: 381–383
Katayama Y, Mori T, Maeda T, Kawamata T (1998) Pathogenesis of the mass effect of cerebral contusions: rapid increase in osmolality within the contusion necrosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 71: 289–292
Kawamata T, Katayama Y, Aoyama N, Mori T (2000) Heterogeneous mechanisms of early edema formation in cerebral contusion: diffusion MRI and ADC mapping study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 76: 9–12
Kawamata T, Katayama Y, Mori T, Aoyama N, Tsubokawa T Jr (2002) Mechanisms of the mass effect of cerebral contusion: ICP monitoring and Diffusion MRI study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 81: 281–283
Lindenberg R, Freytag E (1957) Morphology of cortical contusion. Arch Path 63: 23–42
Maeda T, Katayama Y, Kawamata T, Aoyama N, Mori T (1997) Hemodynamic depression and microthrombosis in the peripheral areas of cortical contusion in the rat: role of platelet activating factor. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 70: 102–105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Maeda, T., Katayama, Y., Kawamata, T., Koyama, S., Sasaki, J. (2003). Ultra-early study of edema formation in cerebral contusion using diffusion MRI and ADC mapping. In: Kuroiwa, T., et al. Brain Edema XII. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements, vol 86. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-0651-8_70
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-0651-8_70
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7220-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-0651-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive