Abstract
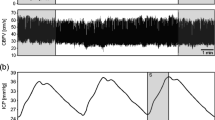
Many data have been published on different methods for measuring “ICP” via ventricular, epidural, subdural or parenchymal record. Also during this meeting, several new devices are presented. However, most investigations only consider the static criteria of the methods, like linearity, zero point stability and hysteresis (Gaab and Heissler 1984, 1988). Little attention has been paid to the dynamic properties of the devices. Such data on frequency resolution (band width) and phase, however, are especially important for computerized evaluation of ICP dynamics including waveform analysis (Chopp and Portnoy 1980; Gaab et al. 1983; Gaab and Heissler 1984, 1988; Portnoy et al. 1983; Varju 1977). ICP pulse waves and the transfer characteristics from arterial blood pressure (SAP) to ICP contain continuous information on intracranial elastance, vasoregulation and CSF dynamics (Branch et al. 1988; Chopp and Portnoy 1980; Portnoy et al. 1983). Dynamic analysis could therefore replace invasive methods like bolus and infusion tests (Anile et al. 1988; Branch et al. 1988; Chopp and Portnoy 1980; Portnoy et al. 1983). However, the waveform investigation e.g., with Fourier transformation up to the 5th harmonic of the ICP pulsation (Piper et al. 1988) requires a bandwidth for recording of > 40 Hz (Gaab and Heissler 1984, 1988). We therefore investigated the frequency resolution and the phase lag of current methods used for measuring ICP and blood pressures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilles D (1978) Die Fouriertransformation in der Signalverarbeitung. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Anile C, Mangiola A, Andreasi F, Branch CA, Portnoy HD (1988) CSF pulse waveform morphology as an indicator of intracranial system impedance: an experimental study. This volume, pp 193–195
Branch CA, Chopp M, Portnoy HD (1988) Fourier analysis of intracranial pressures during experimental intracranial hypertension. This volume, pp 175–180
Burrus ChS, Parks TW (1985) DFT/FFT and convolution algorithms. J Wiley and Sons, New York Toronto
Chopp M, Portnoy HD (1980) Systems analysis of intracranial pressure. Comparison between the volume pressure test and CSF pulse amplitude analysis. J Neurosurg 53: 516–527
Foltz EL, Aine C (1981) Diagnosis of hydrocephalus by CSF pulse wave analysis. A clinical study. Surg Neurol 15: 283–293
Gaab MR, Heissler HE (1984) ICP Monitoring. CRC Crit Rev Biomed Engin 11: 189–250
Gaab MR, Heissler HE (1988) Monitoring Intracranial Pressure. In: Webster JG (ed) Encyclopedia of Medical Devices and Instrumentation. J Wiley and Sons, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto
Gaab MR, Haubitz I, Brawanski A et al. (1983) Pressure-volume diagram, pulse amplitude and intracranial pulse volume. Analysis and significance. In: Ishii S, Nagai H, Brock M (eds) Intracranial Pressure V. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 261–268
Piper IR, Dearden NM, Miller JD (1988) Can waveform analysis of ICP separate vascular from non-vascular causes of intracranial hypertension? This volume, pp 157–163
Portnoy HD, Chopp M, Branch C et al. (1983) CSF pulse wave, ICP and autoregulation. In: Ishii S, Nagai H, Brock M (eds) Intracranial Pressure V. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 180–185
Varju D (1977) Systemtheorie für Biologen und Mediziner. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1989 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gaab, M.R., Heissler, H.E., Ehrhardt, K. (1989). Physical Characteristics of Various Methods for Measuring ICP. In: Hoff, J.T., Betz, A.L. (eds) Intracranial Pressure VII. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-73987-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-73987-3_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-73989-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-73987-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive