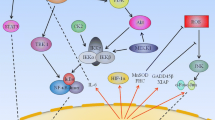
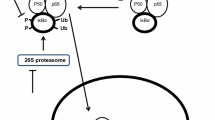
Abstract
The constitutive activation of the transcription factor nuclear-factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a hallmark of many highly malignant tumours such as the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and accounts for profound chemoresistance. Inhibition of NF-κB activation has been shown to be a useful strategy for increasing the sensitivity towards cytostatic drug treatment in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, various pharmacological substances (e.g. thalidomide, bortezomib, sulphasalazine) have already entered clinical studies partially showing promising results for certain types of cancer. Further studies will be needed, in particular for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of appropriate combinations of a NF-κB inhibitor and cytostatic drugs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karin M (2006) Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature 441:431–436
Takada Y, Kobayashi Y, Aggarwal BB (2005) Evodiamine abolishes constitutive and inducible NF-kappaB activation by inhibiting IkappaBalpha kinase activation, thereby suppressing NF-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and metastatic gene expression, up-regulating apoptosis, and inhibiting invasion. J Biol Chem 280:17203–17212
Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB (1998) NF-kappaB and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 16:225–260
Garcea G, Dennison AR, Steward WP, Berry DP (2005) Role of inflammation in pancreatic carcinogenesis and the implications for future therapy. Pancreatology 5:514–529
Farrow B, Evers BM (2002) Inflammation and the development of pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol 10:153–169
Reuther JY, Reuther GW, Cortez D, Pendergast AM, Baldwin AS Jr (1998) A requirement for NF-kappaB activation in Bcr-Abl-mediated transformation. Genes Dev 12:968–981
Ghiorzo P, Mantelli M, Gargiulo S, Gramigni C, Pastorino L, Banelli B, Villaggio B, Coccia MC, Sementa AR, Garre C, Bianchi-Scarra G (2004) Inverse correlation between p16INK4A expression and NF-kappaB activation in melanoma progression. Hum Pathol 35:1029–1037
Sovak MA, Arsura M, Zanieski G, Kavanagh KT, Sonenshein GE (1999) The inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor beta1 on breast cancer cell proliferation are mediated through regulation of aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel expression. Cell Growth Differ 10:537–544
Dejardin E, Deregowski V, Chapelier M, Jacobs N, Gielen J, Merville MP, Bours V (1999) Regulation of NF-kappaB activity by I kappaB-related proteins in adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene 18:2567–2577
Uzzo RG, Crispen PL, Golovine K, Makhov P, Horwitz EM, Kolenko VM (2006) Diverse effects of zinc on NF-kappaB and AP-1 transcription factors: implications for prostate cancer progression. Carcinogenesis 27:1980–1990
Wang W, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB, Larry L, Cleary KR, Chiao PJ (1999) The nuclear factor-kappa B RelA transcription factor is constitutively activated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 5:119–127
Muerkoster S, Arlt A, Sipos B, Witt M, Grossmann M, Kloppel G, Kalthoff H, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2005) Increased expression of the E3-ubiquitin ligase receptor subunit betaTRCP1 relates to constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB activation and chemoresistance in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 65:1316–1324
Arlt A, Vorndamm J, Muerkoster S, Yu H, Schmidt WE, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2002) Autocrine production of interleukin 1beta confers constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity and chemoresistance in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 62:910–916
Niu J, Li Z, Peng B, Chiao PJ (2004) Identification of an autoregulatory feedback pathway involving interleukin-1alpha in induction of constitutive NF-kappaB activation in pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem 279:16452–16462
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS Jr (1996) TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science 274:784–787
Hu L, Shi Y, Hsu JH, Gera J, Van Ness B, Lichtenstein A (2003) Downstream effectors of oncogenic ras in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 101:3126–3135
Zhang H, Ma G, Dong M, Zhao M, Shen X, Ma Z, Guo K (2006) Epidermal growth factor promotes invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells through NF-kappaB-mediated proteinase productions. Pancreas 32:101–109
Liptay S, Weber CK, Ludwig L, Wagner M, Adler G, Schmid RM (2003) Mitogenic and antiapoptotic role of constitutive NF-kappaB/Rel activity in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 105:735–746
Rayet B, Gelinas C (1999) Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 18:6938–6947
Shishodia S, Aggarwal BB (2002) Nuclear factor-kappaB activation: a question of life or death. J Biochem Mol Biol 35:28–40
Packham G, Lahti JM, Fee BE, Gawn JM, Coustan-Smith E, Campana D, Douglas I, Kidd VJ, Ghosh S, Cleveland JL (1997) Fas activates NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis in T-cell lines by signaling pathways distinct from those induced by TNF-alpha. Cell Death Differ 4:130–139
Ivanov VN, Ronai Z (2000) p38 protects human melanoma cells from UV-induced apoptosis through down-regulation of NF-kappaB activity and Fas expression. Oncogene 19:3003–3012
Gupta RA, Polk DB, Krishna U, Israel DA, Yan F, DuBois RN, Peek RM Jr (2001) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma suppresses nuclear factor kappa B-mediated apoptosis induced by Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 276:31059–31066
Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ, Malim MH, Ballard DW (1997) Suppression of tumour necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-kappaB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:10057–10062
Greten FR, Weber CK, Greten TF, Schneider G, Wagner M, Adler G, Schmid RM (2002) Stat3 and NF-kappaB activation prevents apoptosis in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 123:2052–2063
Stehlik C, de Martin R, Kumabashiri I, Schmid JA, Binder BR, Lipp J (1998) Nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-regulated X-chromosome-linked iap gene expression protects endothelial cells from tumour necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med 188:211–216
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS Jr (1998) NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281:1680–1683
Sebens Muerkoster S, Lust J, Arlt A, Hasler R, Witt M, Sebens T, Schreiber S, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2006) Acquired chemoresistance in pancreatic carcinoma cells: induced secretion of IL-1beta and NO lead to inactivation of caspases. Oncogene 25:4628
Muerkoster S, Wegehenkel K, Arlt A, Witt M, Sipos B, Kruse ML, Sebens T, Kloppel G, Kalthoff H, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2004) Tumour stroma interactions induce chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal carcinoma cells involving increased secretion and paracrine effects of nitric oxide and interleukin-1beta. Cancer Res 64:1331–1337
Guo J, Verma UN, Gaynor RB, Frenkel EP, Becerra CR (2004) Enhanced chemosensitivity to irinotecan by RNA interference-mediated down-regulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB p65 subunit. Clin Cancer Res 10:3333–3341
Kalota A, Shetzline SE, Gewirtz AM (2004) Progress in the development of nucleic acid therapeutics for cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 3:4–12
Wall NR, Shi Y (2003) Small RNA: can RNA interference be exploited for therapy? Lancet 362:1401–1403
Pande V, Ramos MJ (2005) NF-kappaB in human disease: current inhibitors and prospects for de novo structure based design of inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 12:357–374
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:17–26
Zavrski I, Jakob C, Schmid P, Krebbel H, Kaiser M, Fleissner C, Rosche M, Possinger K, Sezer O (2005) Proteasome: an emerging target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16:475–481
Al-Aynati MM, Radulovich N, Riddell RH, Tsao MS (2004) Epithelial-cadherin and beta-catenin expression changes in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Clin Cancer Res 10:1235–1240
Koenig A, Mueller C, Hasel C, Adler G, Menke A (2006) Collagen type I induces disruption of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell contacts and promotes proliferation of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 66:4662–4671
Shapiro RS, Anderson KV (2006) Drosophila Ik2, a member of the I kappa B kinase family, is required for mRNA localization during oogenesis. Development 133:1467–1475
Kuranaga E, Kanuka H, Tonoki A, Takemoto K, Tomioka T, Kobayashi M, Hayashi S, Miura M (2006) Drosophila IKK-related kinase regulates nonapoptotic function of caspases via degradation of IAPs. Cell 126:583–596
Oshima K, Takeda M, Kuranaga E, Ueda R, Aigaki T, Miura M, Hayashi S (2006) IKKvarepsilon regulates F actin assembly and interacts with Drosophila IAP1 in cellular morphogenesis. Curr Biol 16:1531–1537
Ikezoe T, Yang Y, Saito T, Koeffler HP, Taguchi H (2004) Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 down-regulates prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and induces growth arrest and apoptosis of androgen-dependent human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Cancer Sci 95:271–275
Cusack JC Jr, Liu R, Houston M, Abendroth K, Elliott PJ, Adams J, Baldwin AS Jr (2001) Enhanced chemosensitivity to CPT-11 with proteasome inhibitor PS-341: implications for systemic nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition. Cancer Res 61:3535–3540
Amiri KI, Horton LW, LaFleur BJ, Sosman JA, Richmond A (2004) Augmenting chemosensitivity of malignant melanoma tumours via proteasome inhibition: implication for bortezomib (VELCADE, PS-341) as a therapeutic agent for malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 64:4912–4918
Denlinger CE, Rundall BK, Keller MD, Jones DR (2004) Proteasome inhibition sensitizes non-small-cell lung cancer to gemcitabine-induced apoptosis. Ann Thorac Surg 78:1207–1214
Fahy BN, Schlieman MG, Mortenson MM, Virudachalam S, Bold RJ (2005) Targeting BCL-2 overexpression in various human malignancies through NF-kappaB inhibition by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 56:46–54
Ma MH, Yang HH, Parker K, Manyak S, Friedman JM, Altamirano C, Wu ZQ, Borad MJ, Frantzen M, Roussos E, Neeser J, Mikail A, Adams J, Sjak-Shie N, Vescio RA, Berenson JR (2003) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 markedly enhances sensitivity of multiple myeloma tumour cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Clin Cancer Res 9:1136–1144
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Richardson PG, Poulaki V, Tai YT, Chauhan D, Fanourakis G, Gu X, Bailey C, Joseph M, Libermann TA, Schlossman R, Munshi NC, Hideshima T, Anderson KC (2003) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 potentiates sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to conventional chemotherapeutic agents: therapeutic applications. Blood 101:2377–2380
Nawrocki ST, Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Bold RJ, Gotsch BS, Abbruzzese JL, Elliott P, Adams J, McConkey DJ (2002) Effects of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 on apoptosis and angiogenesis in orthotopic human pancreatic tumour xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 1:1243–1253
Nawrocki ST, Sweeney-Gotsch B, Takamori R, McConkey DJ (2004) The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib enhances the activity of docetaxel in orthotopic human pancreatic tumour xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3:59–70
Muerkoster S, Arlt A, Witt M, Gehrz A, Haye S, March C, Grohmann F, Wegehenkel K, Kalthoff H, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2003) Usage of the NF-kappaB inhibitor sulfasalazine as sensitizing agent in combined chemotherapy of pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 104:469–476
Heere-Ress E, Boehm J, Thallinger C, Hoeller C, Wacheck V, Birner P, Wolff K, Pehamberger H, Jansen B (2005) Thalidomide enhances the anti-tumour activity of standard chemotherapy in a human melanoma xenotransplantation model. J Invest Dermatol 125:201–206
Son MJ, Kim JS, Kim MH, Song HS, Kim JT, Kim H, Shin T, Jeon HJ, Lee DS, Park SY, Kim YJ, Kim JH, Nam DH (2006) Combination treatment with temozolomide and thalidomide inhibits tumour growth and angiogenesis in an orthotopic glioma model. Int J Oncol 28:53–59
D‘Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E, Folkman J (1994) Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:4082–4085
Gupta D, Treon SP, Shima Y, Hideshima T, Podar K, Tai YT, Lin B, Lentzsch S, Davies FE, Chauhan D, Schlossman RL, Richardson P, Ralph P, Wu L, Payvandi F, Muller G, Stirling DI, Anderson KC (2001) Adherence of multiple myeloma cells to bone marrow stromal cells upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor secretion: therapeutic applications. Leukemia 15:1950–1961
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Shima Y, Raje N, Davies FE, Tai YT, Treon SP, Lin B, Schlossman RL, Richardson P, Muller G, Stirling DI, Anderson KC (2000) Thalidomide and its analogs overcome drug resistance of human multiple myeloma cells to conventional therapy. Blood 96:2943–2950
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, Chauhan D, Richardson PG, Hideshima T, Munshi NC, Treon SP, Anderson KC (2002) Apoptotic signaling induced by immunomodulatory thalidomide analogs in human multiple myeloma cells: therapeutic implications. Blood 99:4525–4530
Marriott JB, Clarke IA, Czajka A, Dredge K, Childs K, Man HW, Schafer P, Govinda S, Muller GW, Stirling DI, Dalgleish AG (2003) A novel subclass of thalidomide analogue with anti-solid tumour activity in which caspase-dependent apoptosis is associated with altered expression of bcl-2 family proteins. Cancer Res 63:593–599
Olsen LS, Hjarnaa PJ, Latini S, Holm PK, Larsson R, Bramm E, Binderup L, Madsen MW (2004) Anticancer agent CHS 828 suppresses nuclear factor-kappa B activity in cancer cells through downregulation of IKK activity. Int J Cancer 111:198–205
Hjarnaa PJ, Jonsson E, Latini S, Dhar S, Larsson R, Bramm E, Skov T, Binderup L (1999) CHS 828, a novel pyridyl cyanoguanidine with potent antitumour activity in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 59:5751–5757
Aleskog A, Bashir-Hassan S, Hovstadius P, Kristensen J, Hoglund M, Tholander B, Binderup L, Larsson R, Jonsson E (2001) Activity of CHS 828 in primary cultures of human hematological and solid tumours in vitro. Anticancer Drugs 12:821–827
Hovstadius P, Lindhagen E, Hassan S, Nilsson K, Jernberg-Wiklund H, Nygren P, Binderup L, Larsson R (2004) Cytotoxic effect in vivo and in vitro of CHS 828 on human myeloma cell lines. Anticancer Drugs 15:63–70
Johanson V, Arvidsson Y, Kolby L, Bernhardt P, Sward C, Nilsson O, Ahlman H (2005) Antitumoural effects of the pyridyl cyanoguanidine CHS 828 on three different types of neuroendocrine tumours xenografted to nude mice. Neuroendocrinology 82:171–176
Martinsson P, Ekelund S, Nygren P, Larsson R (2002) The combination of the antitumoural pyridyl cyanoguanidine CHS 828 and etoposide in vitro—from cytotoxic synergy to complete inhibition of apoptosis. Br J Pharmacol 137:568–573
Wahl C, Liptay S, Adler G, Schmid RM (1998) Sulfasalazine: a potent and specific inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B. J Clin Invest 101:1163–1174
Kopp E, Ghosh S (1994) Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science 265:956–959
Narang VS, Pauletti GM, Gout PW, Buckley DJ, Buckley AR (2003) Suppression of cystine uptake by sulfasalazine inhibits proliferation of human mammary carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 23:4571–4579
Gout PW, Simms CR, Robertson MC (2003) In vitro studies on the lymphoma growth-inhibitory activity of sulfasalazine. Anticancer Drugs 14:21–29
Robe PA, Bentires-Alj M, Bonif M, Rogister B, Deprez M, Haddada H, Khac MT, Jolois O, Erkmen K, Merville MP, Black PM, Bours V (2004) In vitro and in vivo activity of the nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor sulfasalazine in human glioblastomas. Clin Cancer Res 10:5595–5603
Arlt A, Vorndamm J, Breitenbroich M, Folsch UR, Kalthoff H, Schmidt WE, Schafer H (2001) Inhibition of NF-kappaB sensitizes human pancreatic carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by etoposide (VP16) or doxorubicin. Oncogene 20:859–868
Arlt A, Gehrz A, Muerkoster S, Vorndamm J, Kruse ML, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2003) Role of NF-kappaB and Akt/PI3 K in the resistance of pancreatic carcinoma cell lines against gemcitabine-induced cell death. Oncogene 22:3243–3251
Jagannath S, Barlogie B, Berenson J, Siegel D, Irwin D, Richardson PG, Niesvizky R, Alexanian R, Limentani SA, Alsina M, Adams J, Kauffman M, Esseltine DL, Schenkein DP, Anderson KC (2004) A phase 2 study of two doses of bortezomib in relapsed or refractory myeloma. Br J Haematol 127:165–172
Oakervee HE, Popat R, Curry N, Smith P, Morris C, Drake M, Agrawal S, Stec J, Schenkein D, Esseltine DL, Cavenagh JD (2005) PAD combination therapy (PS-341/bortezomib, doxorubicin and dexamethasone) for previously untreated patients with multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 129:755–762
Richardson PG, Sonneveld P, Schuster MW, Irwin D, Stadtmauer EA, Facon T, Harousseau JL, Ben-Yehuda D, Lonial S, Goldschmidt H, Reece D, San-Miguel JF, Blade J, Boccadoro M, Cavenagh J, Dalton WS, Boral AL, Esseltine DL, Porter JB, Schenkein D, Anderson KC (2005) Bortezomib or high-dose dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 352:2487–2498
Richardson PG, Briemberg H, Jagannath S, Wen PY, Barlogie B, Berenson J, Singhal S, Siegel DS, Irwin D, Schuster M, Srkalovic G, Alexanian R, Rajkumar SV, Limentani S, Alsina M, Orlowski RZ, Najarian K, Esseltine D, Anderson KC, Amato AA (2006) Frequency, characteristics, and reversibility of peripheral neuropathy during treatment of advanced multiple myeloma with bortezomib. J Clin Oncol 24:3113–3120
Goy A, Younes A, McLaughlin P, Pro B, Romaguera JE, Hagemeister F, Fayad L, Dang NH, Samaniego F, Wang M, Broglio K, Samuels B, Gilles F, Sarris AH, Hart S, Trehu E, Schenkein D, Cabanillas F, Rodriguez AM (2005) Phase II study of proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin‘s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23:667–675
O‘Connor OA, Wright J, Moskowitz C, Muzzy J, MacGregor-Cortelli B, Stubblefield M, Straus D, Portlock C, Hamlin P, Choi E, Dumetrescu O, Esseltine D, Trehu E, Adams J, Schenkein D, Zelenetz AD (2005) Phase II clinical experience with the novel proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin‘s lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23:676–684
Maki RG, Kraft AS, Scheu K, Yamada J, Wadler S, Antonescu CR, Wright JJ, Schwartz GK (2005) A multicenter Phase II study of bortezomib in recurrent or metastatic sarcomas. Cancer 103:1431–1438
Mackay H, Hedley D, Major P, Townsley C, Mackenzie M, Vincent M, Degendorfer P, Tsao MS, Nicklee T, Birle D, Wright J, Siu L, Moore M, Oza A (2005) A phase II trial with pharmacodynamic endpoints of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:5526–5533
Markovic SN, Geyer SM, Dawkins F, Sharfman W, Albertini M, Maples W, Fracasso PM, Fitch T, Lorusso P, Adjei AA, Erlichman C (2005) A phase II study of bortezomib in the treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma. Cancer 103:2584–2589
Shah MH, Young D, Kindler HL, Webb I, Kleiber B, Wright J, Grever M (2004) Phase II study of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341) in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumours. Clin Cancer Res 10:6111–6118
Aghajanian C, Dizon DS, Sabbatini P, Raizer JJ, Dupont J, Spriggs DR (2005) Phase I trial of bortezomib and carboplatin in recurrent ovarian or primary peritoneal cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:5943–5949
Alberts SR, Foster NR, Morton RF, Kugler J, Schaefer P, Wiesenfeld M, Fitch TR, Steen P, Kim GP, Gill S (2005) PS-341 and gemcitabine in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a North Central Cancer Treatment Group (NCCTG) randomized phase II study. Ann Oncol 16:1654–1661
Singhal S, Mehta J, Desikan R, Ayers D, Roberson P, Eddlemon P, Munshi N, Anaissie E, Wilson C, Dhodapkar M, Zeddis J, Barlogie B (1999) Antitumour activity of thalidomide in refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 341:1565–1571
Rajkumar SV, Blood E, Vesole D, Fonseca R, Greipp PR (2006) Phase III clinical trial of thalidomide plus dexamethasone compared with dexamethasone alone in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a clinical trial coordinated by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 24:431–436
Wang M, Weber DM, Delasalle K, Alexanian R (2005) Thalidomide-dexamethasone as primary therapy for advanced multiple myeloma. Am J Hematol 79:194–197
Badros AZ, Goloubeva O, Rapoport AP, Ratterree B, Gahres N, Meisenberg B, Takebe N, Heyman M, Zwiebel J, Streicher H, Gocke CD, Tomic D, Flaws JA, Zhang B, Fenton RG (2005) Phase II study of G3139, a Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide, in combination with dexamethasone and thalidomide in relapsed multiple myeloma patients. J Clin Oncol 23:4089–4099
Kyriakou C, Thomson K, D‘Sa S, Flory A, Hanslip J, Goldstone AH, Yong KL (2005) Low-dose thalidomide in combination with oral weekly cyclophosphamide and pulsed dexamethasone is a well tolerated and effective regimen in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 129:763–770
Eisen T, Boshoff C, Mak I, Sapunar F, Vaughan MM, Pyle L, Johnston SR, Ahern R, Smith IE, Gore ME (2000) Continuous low dose thalidomide: a phase II study in advanced melanoma, renal cell, ovarian and breast cancer. Br J Cancer 82:812–817
Reiriz AB, Richter MF, Fernandes S, Cancela AI, Costa TD, Di Leone LP, Schwartsmann G (2004) Phase II study of thalidomide in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res 14:527–531
McCollum AD, Wu B, Clark JW, Kulke MH, Enzinger PC, Ryan DP, Earle CC, Michelini A, Fuchs CS (2006) The combination of capecitabine and thalidomide in previously treated, refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 29:40–44
Kulke MH, Stuart K, Enzinger PC, Ryan DP, Clark JW, Muzikansky A, Vincitore M, Michelini A, Fuchs CS (2006) Phase II study of temozolomide and thalidomide in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumours. J Clin Oncol 24:401–406
Gordon JN, Trebble TM, Ellis RD, Duncan HD, Johns T, Goggin PM (2005) Thalidomide in the treatment of cancer cachexia: a randomised placebo controlled trial. Gut 54:540–545
Zhou W, Jiang ZW, Jiang J, Li N, Li JS (2004) Role of NF-kappa B in cancer cachexia [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 42:683–686
Hovstadius P, Larsson R, Jonsson E, Skov T, Kissmeyer AM, Krasilnikoff K, Bergh J, Karlsson MO, Lonnebo A, Ahlgren J (2002) A Phase I study of CHS 828 in patients with solid tumour malignancy. Clin Cancer Res 8:2843–2850
Ravaud A, Cerny T, Terret C, Wanders J, Bui BN, Hess D, Droz JP, Fumoleau P, Twelves C (2005) Phase I study and pharmacokinetic of CHS-828, a guanidino-containing compound, administered orally as a single dose every 3 weeks in solid tumours: an ECSG/EORTC study. Eur J Cancer 41:702–707
Binderup E, Bjorkling F, Hjarnaa PV, Latini S, Baltzer B, Carlsen M, Binderup L (2005) EB1627: a soluble prodrug of the potent anticancer cyanoguanidine CHS828. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:2491–2494
Robe PA, Martin D, Albert A, Deprez M, Chariot A, Bours V (2006) A phase 1–2, prospective, double blind, randomized study of the safety and efficacy of Sulfasalazine for the treatment of progressing malignant gliomas: study protocol of [ISRCTN45828668]. BMC Cancer 6:29
Muerkoster S, Arlt A, Gehrz A, Vorndamm J, Witt M, Grohmann F, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2004) Autocrine IL-1beta secretion leads to NF-kappabeta-mediated chemoresistance in pancreatic carcinoma cells in vivo [in German]. Med Klin (Munich) 99:185–190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sebens, S., Arlt, A., Schäfer, H. (2008). NF-κ B as a Molecular Target in the Therapy of Pancreatic Carcinoma. In: Pancreatic Cancer. Recent Results in Cancer Research, vol 177. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71279-4_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71279-4_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-71266-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-71279-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)