Summary
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is an important invasive monitoring parameter in management of patients with acute brain injury and compromised compliance. This study aimed to compare waveforms obtained from standard ICP monitoring and noninvasive ICP monitoring (nICP) methods.
We analyzed continuous arterial blood pressure (ABP) waves, ICP (with standard monitoring), and nICP recorded simultaneously. All signal recordings were sliced into data chunks, each 1 min in duration, and from the mean pulse, we determined the time to peak (Tp) and the ratio between tidal and percussion waves (P2/P1). We also calculated the Isomap projection of the pulses into a bidimensional space—K1 and K2. The defined nICP and ICP parameters were compared using a unilateral Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test. The Pearson correlation coefficient and normalized mutual information were used to verify the association between parameters.
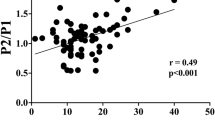
In total, 1504 min of monitoring from ten patients were studied. Nine of the patients were male. The mean age of the patients was 58.4 ± 10.4 years, and they had an initial Glasgow Coma Scale of 9 ± 4, a mean Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) of 45.6, and an intensive care unit stay of 44 ± 45 days. With the exception of Tp, all parameters showed a weak linear association but presented a strong nonlinear association.
Mutual information analysis and a bigger sample size would be helpful to build more refined models and to improve understanding of the waveform relationships.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawoos U, McCarron RM, Auker CR, Chavko M (2015) Advances in intracranial pressure monitoring and its significance in managing traumatic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci 16(12):28979–28997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226146
Hastie T, Tibshirani R, Friedman J (2013) The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. Springer, New York
Benitez D, Gaydecki PA, Zaidi A, Fitzpatrick AP (2001) The use of the Hilbert transform in ECG signal analysis. Comput Biol Med 31:399–406
Mitrou N, Laurin A, Dick T, Inskip J (2017) A peak detection method for identifying phase in physiological signals. Biomed Signal Process Control 31:452–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2016.07.001
Zoubir AM, Boashash B (1998) The bootstrap and its application in signal processing. IEEE Signal Process Mag 15:56–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/79.647043
Tenenbaum JB (2000) A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290:2319–2323. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5500.2319
Oliphant TE (2015) Guide to NumPy, 2nd edn. Continuum, Austin
Oliphant TE (2007) Python for scientific computing. Comput Sci Eng 9:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcse.2007.58
Garreta R, Moncecchi G (2013) Learning scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. Packt, Birmingham
Hunter JD (2007) Matplotlib: a 2D graphics environment. Comput Sci Eng 9(3):90–95. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcse.2007.55
Vu T, Mishra A, Konapala G (2018) Information entropy suggests stronger nonlinear associations between hydro-meteorological variables and ENSO. Entropy 20(1):38
Strong SP, Koberle R, Van Steveninck RRDR, Bialek W (1998) Entropy and information in neural spike trains. Phys Rev Lett 80(1):197
Frigieri G, Andrade RAP, Dias C, Spavieri DL Jr, Brunelli R, Cardim DA, Wang CC, Verzola RMM, Mascarenhas S (2018) Analysis of a non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring method in patients with traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl 126:107–110
Vilela GH, Cabella B, Mascarenhas S et al (2016) Validation of a new minimally invasive intracranial pressure monitoring method by direct comparison with an invasive technique. Acta Neurochir Suppl 122:97–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Juliana Shibaki, Bruno Padua, Felipe Silva, Thauan Gonçalves, Deusdedit Spavieri-Junior, Gustavo Frigieri, and Sérgio Mascarenhas have received financial support from Braincare Health Technologies. Inês Gomes and Celeste Dias have no commercial relationship with the company.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gomes, I. et al. (2021). Comparison of Waveforms Between Noninvasive and Invasive Monitoring of Intracranial Pressure. In: Depreitere, B., Meyfroidt, G., Güiza, F. (eds) Intracranial Pressure and Neuromonitoring XVII. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement, vol 131. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59436-7_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59436-7_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59435-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59436-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)