Abstract
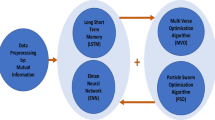
Deep learning, as one of the most popular techniques, is able to efficiently train a model on big data by using large-scale optimization algorithms. Although there exist some works applying machine learning to air quality prediction, most of the prior studies are restricted to several-year data and simply train standard regression models (linear or nonlinear) to predict the hourly air pollution concentration. The main purpose of this proposal is design predictor to accurately forecast air quality indices (AQIs) of the future 48 h. Accurate predictions of AQIs can bring enormous value to governments, enterprises, and the general public -and help them make informed decisions. We Will Build Model Consist of four Steps: (A) Determine the Main Rules (contractions) of avoiding emission (B) Obtaining and pre-processing reliable database from (KDD CUP 2018) (C) Building Predator have multi-level based on Long Short-term Memory network corporative with one of optimization algorithm called (Partial Swarm) to predict the PM2.5, PM10, and O3 concentration levels over the coming 48 h for every measurement station. (D) To evaluate the predictions, on each day, SMAPE scores will be calculated for each station, each hour of the day (48 h overall), and each pollutant (PM2.5, PM10, SOx, CO, O3 and NOx). The daily SMAPE score will then be the average of all the individual SMAPE scores.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ong, B.T., Sugiura, K., Zettsu, K.: Dynamically Pre-Trained Deep Recurrent Neural Networks using environmental monitoring Data for Predicting PM2.5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1955-3
Al-Janabi, S., Rawat, S., Patel, A., Al-Shourbaji, I.: Design and evaluation of a hybrid system for detection and prediction of faults in electrical transformers. Int. J. Electri. Power Energy Syst. 67, 324–335 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.12.005
Li, X., Peng, L., Hu, Y., Shao, J., Chi, T.: Deep learning architecture for Air quality predictions. Environ. Pollut. 231, 997–1004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7812-9
Li, X., Peng, L., Yao, X., Cui, S., Hu, Y., You, C., Chi, T.: Long short-term memory neural network for air pollutant concentration predictions: Method development and evaluation. Environ. Pollut. 997–1004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.114
Ghoneim, O.A., Manjunatha, B.R.: Forecasting of Ozone Concentration in Smart City using Deep Learning, pp. 1320–1326 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2017.8126024
Lifeng, W., Li, N., Yang, Y.: Prediction of air quality indicators for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Clean. Prod. 196(2018), 682–687 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.068
Popoola, O.A.M., Carruthers, D., Lad, C., Bright, V.B., Mead, M.I., Stettler, M.E.J., Saffell, J.R., Jones, R.L.: Use of networks of low-cost air quality sensors to quantify air quality in urban settings. Atmos. Environ. 194, 58–70 (2018)
Wen, C., Liu, S., Yao, X., Peng, L., Li, X., Hu, Y., Chi, T.: A novel spatiotemporal convolutional long short-term neural network for air pollution prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 654, 1091–1099 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.086
Shang, Z., Deng, T., He, J., Duan, X.: A novel model for hourly PM2.5 concentration prediction based on CART and EELM. Sci. Total Environ. 651, 3043–3052 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.193
Li, H., Wang, J., Li, R., Haiyan, L.: Novel analysis forecast system based on multi-objective optimization for air quality index. Clean. Prod. 208, 1365–1383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.129
Buyya, R., Calheiros, R.N., Astjerdi, A.V.: Big data: principles and paradigms. Big Data: Principles and Paradigms, pp. 1–468 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/c2015-0-04136-3
Oussous, A., Benjelloun, F.-Z., Lahcen, A.A., Belfkih, S.: Big data technologies. Adv. Parallel Comput. 28–55 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3233/978-1-61499-814-3-28
Liu, S., Wang, Y., Yang, X., Lei, B., Liu, L., Li, S.X., Ni, D., Wang, T.: Deep learning in medical ultrasound analysis: a review. Engineering (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.020
Al-Janabi, S., Alkaim, A.F.: A nifty collaborative analysis to predicting a novel tool (DRFLLS) for missing values estimation. J. Soft Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-03972-x. Springer
Aunan, K., Hansen, M., Liu, Z., Wang, S.: The hidden hazard of household air pollution in Rural China. Environ. Sci. Policy 93, 27–33 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2018.12.004
Inácio, F., Macharet, D., Chaimowicz, L.: PSO-based strategy for the segregation of heterogeneous ro Botic swarms. J. Comput. Sci. 86–94 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2018.12.008
Matos, J., Faria, R., Nogueira, I., Loureiro, J., Ribeiro, A.: Optimization strategies for chiral separation by true moving bed chromatography using Particles Swarm Optimization (PSO) and new Parallel PSO variant. Comput. Chem. Eng. 344–356 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/jcompchemeng.2019.01.020
Hu, M., Wang, H., Wang, X., Yang, J., Wang, R.: Video facial emotion recognition based on local en Hanced motion history image and CNN-CTSLSTM networks. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 176–185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.12.039
Al_Janabi, S., Mahdi, M.A.: Evaluation prediction techniques to achievement an optimal biomedical analysis. Int. J. Grid Util. Comput. (2019)
Al-Janabi, S., Alwan, E.: Soft mathematical system to solve black box problem through development the FARB based on hyperbolic and polynomial functions. In: IEEE, 2017 10th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), Paris, pp. 37–42 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/dese.2017.23
Al_Janabi, S., Al_Shourbaji, I., Salman, M.A.: Assessing the suitability of soft computing approaches for forest fires prediction. Appl. Comput. Inf. 14(2), 214–224 (2018). ISSN 2210-8327, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aci.2017.09.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval:
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the author.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Al_Janabi, S., Yaqoob, A., Mohammad, M. (2020). Pragmatic Method Based on Intelligent Big Data Analytics to Prediction Air Pollution. In: Farhaoui, Y. (eds) Big Data and Networks Technologies. BDNT 2019. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 81. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23672-4_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23672-4_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-23671-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-23672-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)