Abstract
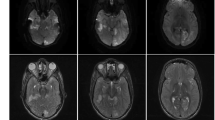
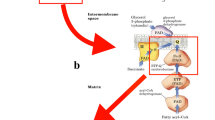
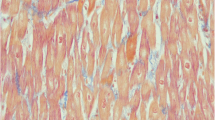
Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase (CACT) deficiency is a rare long-chain fatty acid oxidation disorder (LC-FAOD) with high mortality due to cardiomyopathy or lethal arrhythmia. Triheptanoin (UX007), an investigational drug composed of synthetic medium odd-chain triglycerides, is a novel therapy in development for LC-FAOD patients. However, cases of its safe and efficacious use to reverse severe heart failure in CACT deficiency are limited. Here, we present a detailed report of an infant with CACT deficiency admitted in metabolic crisis that progressed into severe cardiogenic shock who was successfully treated by triheptanoin. The child was managed, thereafter, on triheptanoin until her death at 3 years of age from a cardiopulmonary arrest in the setting of acute respiratory illness superimposed on chronic hypercarbic respiratory failure.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonnet D, Martin D, Pascale De L, Villain E, Jouvet P, Rabier D, Brivet M, Saudubray JM (1999) Arrhythmias and conduction defects as presenting symptoms of fatty acid oxidation disorders in children. Circulation 100:2248–2253
Eto K, Sakai N, Shimada S, Shioda M, Ishigaki K, Hamada Y, Shinpo M, Azuma J, Tominaga K, Shimojima K, Ozono K, Osawa M, Yamamoto T (2013) Microdeletions of 3p21.31 characterized by developmental delay, distinctive features, elevated serum creatine kinase levels, and white matter involvement. Am J Med Genet A 161a:3049–3056
Haldeman-Englert CR, Gai X, Perin JC, Ciano M, Halbach SS, Geiger EA, McDonald-McGinn DM, Hakonarson H, Zackai EH, Shaikh TH (2009) A 3.1-Mb microdeletion of 3p21.31 associated with cortical blindness, cleft lip, CNS abnormalities, and developmental delay. Eur J Med Genet 52:265–268
Hsu BY, Iacobazzi V, Wang Z, Harvie H, Chalmers RA, Saudubray JM, Palmieri F, Ganguly A, Stanley CA (2001) Aberrant mRNA splicing associated with coding region mutations in children with carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab 74:248–255
Pande SV, Murthy MS (1994) Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency: implications in human pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1226:269–276
Roe CR, Brunengraber H (2015) Anaplerotic treatment of long-chain fat oxidation disorders with triheptanoin: review of 15 years experience. Mol Genet Metab 116:260–268
Roe CR, Mochel F (2006) Anaplerotic diet therapy in inherited metabolic disease: therapeutic potential. J Inherit Metab Dis 29:332–340
Roe CR, Sweetman L, Roe DS, David F, Brunengraber H (2002) Treatment of cardiomyopathy and rhabdomyolysis in long-chain fat oxidation disorders using an anaplerotic odd-chain triglyceride. J Clin Invest 110:259–269
Rubio-Gozalbo ME, Bakker JA, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ (2004) Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency, clinical, biochemical and genetic aspects. Mol Asp Med 25:521–532
Spiekerkoetter U, Lindner M, Santer R, Grotzke M, Baumgartner MR, Boehles H, Das A, Haase C, Hennermann JB, Karall D, de Klerk H, Knerr I, Koch HG, Plecko B, Roschinger W, Schwab KO, Scheible D, Wijburg FA, Zschocke J, Mayatepek E, Wendel U (2009) Management and outcome in 75 individuals with long-chain fatty acid oxidation defects: results from a workshop. J Inherit Metab Dis 32:488–497
Stanley CA, Hale DE, Berry GT, Deleeuw S, Boxer J, Bonnefont JP (1992) Brief report: a deficiency of carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase in the inner mitochondrial membrane. N Engl J Med 327:19–23
Vitoria I, Martin-Hernandez E, Pena-Quintana L, Bueno M, Quijada-Fraile P, Dalmau J, Molina-Marrero S, Perez B, Merinero B (2015) Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency: experience with four cases in Spain and review of the literature. JIMD Rep 20:11–20
Vockley J, Marsden D, McCracken E, DeWard S, Barone A, Hsu K, Kakkis E (2015) Long-term major clinical outcomes in patients with long chain fatty acid oxidation disorders before and after transition to triheptanoin treatment – a retrospective chart review. Mol Genet Metab 116:53–60
Vockley J, Charrow J, Ganesh J, Eswara M, Diaz GA, McCracken E, Conway R, Enns GM, Starr J, Wang R, Abdenur JE, Sanchez-de-Toledo J, Marsden DL (2016) Triheptanoin treatment in patients with pediatric cardiomyopathy associated with long chain-fatty acid oxidation disorders. Mol Genet Metab 119:223–231
Vockley J, Burton B, Berry GT, Longo N, Phillips J, Sanchez-Valle A, Tanpaiboon P, Grunewald S, Murphy E, Humphrey R, Mayhew J, Bowden A, Zhang L, Cataldo J, Marsden DL, Kakkis E (2017) UX007 for the treatment of long chain-fatty acid oxidation disorders: safety and efficacy in children and adults following 24 weeks of treatment. Mol Genet Metab 120(4):370–377
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by: Manuel Schiff
Appendices
Synopsis
This report details the safe use of triheptanoin to reverse cardiogenic shock in the case of a patient with carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency suffering severe metabolic crisis devolving into acute heart failure.
Compliance with Ethical Guidelines
As the submitting author, I confirm that all authors have adhered to strict ethical guidelines in the generation of this manuscript.
Contributor’s Statement
Sidharth Mahapatra contributed to the conception and design of this case presentation, the literature search, drafting the initial manuscript, and revising and reviewing the manuscript.
Amitha Ananth, Nancy Baugh, and Mihaela Damian reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Mihaela Damian contributed to the conception and design of the case presentation and gathered the data to generate the tables and figure.
Gregory Enns contributed to the conception and design of the case presentation, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. He was a member of the UX007 data safety monitoring board.
All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 SSIEM and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mahapatra, S., Ananth, A., Baugh, N., Damian, M., Enns, G.M. (2017). Triheptanoin: A Rescue Therapy for Cardiogenic Shock in Carnitine-acylcarnitine Translocase Deficiency. In: Morava, E., Baumgartner, M., Patterson, M., Rahman, S., Zschocke, J., Peters, V. (eds) JIMD Reports, Volume 39. JIMD Reports, vol 39. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2017_36
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2017_36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-57576-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-57577-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)