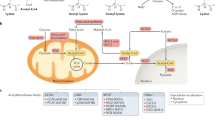
Post-translational modifications of nonhistone proteins play a significant role in regulating the chromatin structure, dynamics and thereby gene regulation. Among the different posttranslational modifications, reversible acetylation of non-histone proteins has profound functional implications on wide range of cellular processes. The acetylation status of these proteins is regulated by several cellular and non-cellular factors like viruses, physiological stresses, DNA damaging agents and ROS. Mutations found in the acetylation sites of these proteins and aberrant acetylation are related to imbalances in different cellular pathways and various diseases. Several factor acetyltransferases and deacetylases are known to regulate the acetylation of the nonhistone proteins. Modulators of these enzymes derived from natural as well as synthetic sources can thus have important therapeutic implications. Designing strategies to specifically target the acetylation of these proteins can be used as a valuable tool for new generation drugs
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee S, Kumar BRP, Kundu TK (2004) General transcriptional coactivator PC4 activates p53 function. Mol Cell Biol 24(5): 2052–2062
Bedford MT, Richard S (2005) Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol Cell 18(3): 263–272
Bergel M, Herrera JE, Thatcher BJ, Prymakowska-Bosak M, Vassilev A, Nakatani Y, Martin B, Bustin M (2000) Acetylation of novel sites in the nucleosomal binding domain of chromosomal protein HMG-14 by p300 alters its interaction with nucleosomes. J Biol Chem 275(15): 11514–11520
Bhakat KK, Hazra TK, Mitra S (2004) Acetylation of the human DNA glycosylase NEIL2 and inhibition of its activity. Nucleic Acids Research 32(10): 3033–3039
Blander G, Zalle N, Daniely Y, Taplick J, Gray MD (2002). DNA Damage-induced Translocation of the Werner helicase is regulated by acetylation. J Biol Chem 277(52): 50934–50940
Bode AM, Dong Z (2004) Post-translational modification of p53 in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 4(10): 793–805
Catez F, Lim JH, Hock R, Postnikov YV, Bustin M. (2003) HMGN dynamics and chromatin function. Biochem Cell Biol 81: 113–122
Cereseto A, Manganaro L, Gutierrez MI, Terreni M, Fittipaldi A, Lusic M, Marcello A, Giacca M (2005) Acetylation of HIV-1 integrase by p300 regulates viral integration. EMBOJ 24(17): 3070–3081
Chen LF, Greene WC (2004) Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(5): 392–401
Chen X, Bieker JJ (2004) Stage-specific repression by the EKLF transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol 24(23): 10416–10424
Choi CH, Burton ZF, Usheva A (2004) Auto-acetylation of transcription factors as a control mechanism in gene expression. Cell Cycle 3(2): 114–115
Clevers H (2004) Wnt breakers in colon cancer. Cancer Cell 5(1): 5–6
Cohen HY, Lavu S, Bitterman KJ, Hekking B, Imahiyerobo TA, Miller C, Frye R, Ploegh H, Kessler BM, Sinclair DA (2004) Acetylation of the C terminus of Ku70 by CBP and PCAF controls Bax-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell 13(5): 627–638
Corda D, Colanzi A, Luini A (2006) The multiple activities of CtBP/BARS proteins: the Golgi view. Trends Cell Biol 16(3): 167–173
Cosma MP, Tanaka T, Nasmyth K (1999) Ordered recruitment of transcription and chromatin remodeling factors to a cell cycle- and developmentally regulated promoter. Cell 97: 299–311
Costanzo A, Merlo P, Pediconi N, Fulco M, Sartorelli V, Cole PA, Fontemaggi G, Fanciulli M, Schiltz L, Blandino G, Balsano C, Levrero M (2002) DNA damage-dependent acetylation of p73 dictates the selective activation of apoptotic target genes. Mol Cell 9(1): 75–86
Davie JR, Hendzel MJ (1994) Multiple functions of dynamic histone acetylation. J Cell Biochem 55(1): 98–105
Deng L, de la Fuente C, Fu P, Wang L, Donnelly R, Wade JD, Lambert P, Li H, Lee CG, Kashanchi F (2000) Acetylation of HIV-1 Tat by CBP/P300 increases transcription of integrated HIV-1 genome and enhances binding to core histones. Virology 277(2): 278–295
Deng L, Wang D, de la Fuente C, Wang L, Li H, Lee CG, Donnelly R, Wade JD, Lambert P, Kashanchi F (2001) Enhancement of the p300 HAT activity by HIV-1 Tat on chromatin DNA. Virology 289(2): 312–326
Faiola F, Liu X, Lo S, Pan S, Zhang K, Lymar E, Farina A, Martinez E. (2005) Dual regulation of c-Myc by p300 via acetylation-dependent control of Myc protein turnover and coactivation of Myc-induced transcription. Mol Cell Biol 25(23): 10220–10234
Fiordaliso F, Leri A, Cesselli D, Limana F, Safai B, Nadal-Ginard B, Anversa P, Kajstura J (2001) Hyperglycemia activates p53 and p53-regulated genes leading to myocyte cell death. Diabetes 50(10): 2363–2375
Forrest AR, Taylor DF, Crowe ML, Chalk AM, Waddell NJ, Kolle G, Faulkner GJ, Kodzius R, Katayama S, Wells C, Kai C, Kawai J, Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y, Grimmond SM (2006) Genome-wide review of transcriptional complexity in mouse protein kinases and phosphatases. Genome Biol 7 R5
Fu M, Wang C, Wang J, Zhang X, Sakamaki T, Yeung YG, Chang C, Hopp T, Fuqua SA, Jaffray E, Hay RT, Palvimo JJ, Janne OA, Pestell RG (2002) Androgen receptor acetylation governs trans activation and MEKK1-induced apoptosis without affecting in vitro sumoylation and trans-repression function. Mol Cell Biol 22(10): 3373–3388
Galbiati L, Mendoza-Maldonado R, Gutierrez MI, Giacca M (2005) Regulation of E2F-1 after DNA damage by p300-mediated acetylation and ubiquitination. Cell Cycle 4(7): 930–939
Gay F, Calvo D, LO MC, Ceron J, Maduro M, Lin R, Shi Y (2003) Acetylation regulates subcellular localization of the Wnt signaling nuclear effector POP-1. Genes Dev 17(6): 717–722
Ghazaleh Sadri-Vakili, Jang-Ho J Cha (2006) Mechanisms of Disease: Histone modifications in Huntington’s disease. Nature Clinical Practice Neurology 2: 330–338
Gong JG, Costanzo A, Yang HQ, Melino G, Kaelin WG Jr, Levrero M, Wang JY (1999) The tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Nature 399(6738): 734–735, 737
Grunstein M (1999) Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature 389: 349–352
Gu W, Roeder RG (1997) Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal domain. Cell 90(4): 595–606
Hasan S, El-Andaloussi N, Hardeland U, Hassa PO, Burki C, Imhof R, Schar P, Hottiger MO (2002) Acetylation regulates the DNA end-trimming activity of DNA polymerase beta. Mol Cell 10(5): 1213–1222
Hassa PO, Haenni SS, Buerki C, Meier NI, Lane WS, Owen H, Gersbach M, Imhof R, Hottiger MO (2005) Acetylation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 by p300/CREB-binding protein regulates coactivation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. J Biol Chem 280(49): 40450–40464
Herrera JE, Bergel M, Yang XJ Nakatani Y, Bustin M (1997) The histone acetyltransferase activity of human GCN5 and PCAF is stabilized by coenzymes. J Biol Chem 272(43): 27253–27258
Herrera JE, Sakaguchi K, Bergel M, Trieschmann L, Nakatani Y, Bustin M (1999) Specific acetylation of chromosomal protein HMG-17 by PCAF alters its interaction with nucleosomes. Mol Cell Biol 19(5): 3466–3473
Hong W, Kim AY, Ky S, Rakowski C, Seo SB, Chakravarti D, Atchison M, Blobel GA (2002) Inhibition of CBP-mediated protein acetylation by the Ets family oncoprotein PU.1. Mol Cell Biol 22(11): 3729–3743
Huang BH, Laban M, Leung CH, Lee L, Lee CK Salto-Tellez M, Raju GC, Hooi SC (2005) Inhibition of histone deacetylase increases apoptosis and p21(Cip1/WAF1) expression, independent of histone deacetylase. Cell death differ 12(4): 395–404
Imhof A, Yang XJ, Ogryzko VV, Nakatani Y, Wolffe AP, Ge H (1997) Acetylation of general transcription factors by histone acetyltransferases. Curr Biol 7(9): 689–692
Ito A, Kawaguchi Y, Lai CH, Kovacs JJ, Higashimoto Y, Appella E, Yao TP (2002) MDM2-HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of p53 is required for its degradation. EMBO 21(22): 6236–6245
Ito T, Ikehara T, Nakagawa T, Kraus WL, Muramatsu M (2000) p300-mediated acetylation facilitates the transfer of histone H2A-H2B dimers from nucleosomes to a histone chaperone. Genes Dev.14(15): 1899–1907
Jackson V, Shires A, Tanphaichitr N, Chalkley R (1976) Modifications to histones immediately after synthesis. J Mol Biol 104(2): 471–483
Jacob AL, Lund J, Martinez P, Hedin L (2001) Acetylation of steroidogenic factor 1 protein regulates its transcriptional activity and recruits the coactivator GCN5. J Biol Chem 276(40): 37659–37664
Jeong JW, Bae MK, Ahn MY, Kim SH, Sohn TK, Bae MH, Yoo MA, Song EJ, Lee KJ, Kim KW (2002) Regulation and destabilization of HIF-1alpha by ARD1-mediated acetylation. Cell 111(5): 709–720
Jin Y, Zeng SX, Dai MS, Yang XJ, Lu H (2002) MDM2 Inhibits PCAF (p300/CREB-binding Protein-associated Factor)-mediated p53 Acetylation. J Biol Chem 277(34): 30838–30843
Kaiser C, James SR (2004) Acetylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 is permissive for tyrosine phosphorylation. BMC Biol. 2:23
Kawaguchi Y, Ito A, Appella E, Yao TP (2006) Charge modification at multiple C-terminal lysine residues regulates p53 oligomerization and its nucleus-cytoplasm trafficking 281(3): 1394–1400
Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1996) Life (and death) in a malignant tumour. Nature 379(6560): 19–20
Keizo Nishikawa, Makoto Kobayashi, Atsuko Masumi, Susan E Lyons, Brant M Weinstein, Paul Liu P, Masayuki Yamamoto (2003) Self-association of gata1 enhances transcriptional activity in vivo in Zebra Fish embryos. Mol Cell Biol 23: 8295–8305
Knights CD, Catania J, Giovanni SD, Muratoglu S, Perez R, Swartzbeck A, Quong AA, Zhang X, Beerman T, Pestell RG, Avantaggiati ML (2006) Distinct p53 acetylation cassettes differentially influence gene-expression patterns and cell fate. J Cell Biol 173(4): 533–544
Kobayashi Y, Furukawa-Hibi Y, Chen C, Horio Y, Isobe K, Ikeda K, Motoyama N (2005) SIRT1 is critical regulator of FOXO-mediated transcription in response to oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med 16(2): 237–243
Kovacs JJ Cohen TJ Yao TP (2005) Chaperoning steroid hormone signaling via reversible acetylation. Nucl Recept Signal. 3: e004
Kramer OH, Baus D, Knauer SK, Stein S, Jager E, Stauber RH, Grez M, Pfitzner E, Heinzel T (2006) Acetylation of Stat1 modulates NF-kappaB activity. Genes Dev 20(4): 473–485
Kumar BR, Swaminathan V, Banerjee S , Kundu TK (2001) p300-mediated acetylation of human transcriptional coactivator PC4 is inhibited by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 276(20): 16804–16809
Lim JH, West KL, Rubinstein Y, Bergel M, Postnikov YV, Bustin M (2005) Chromosomal protein HMGN1 enhances the acetylation of lysine 14 in histone H3. EMBO J 24(17): 3038–3048
Li M, Luo J, Brooks CL, Gu W (2002) Acetylation of p53 inhibits its ubiquitination by Mdm2. J Biol Chem 277(52) 50607–50611
Lu Q, Hutchins AE, Doyle CM, Lundblad JR, Kwok RP (2003) Acetylation of CAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) by CREB-binding protein enhances (REB-dependent Transcription. J Biol Chem. 278(18): 15727–15734
Lucey MJ, Chen D, Garcia JL, Hart SM, Phoenix F, Jehani RA, Alao JP, White R, Kindle RB, Losson R, Chambon P, Parker MG, Schär P, Heery DM, Buluwelan L, Ali S (2005) T:G mismatch-specific thymine-DNA glycosylase (TDG) as a coregulator of transcription interacts with SRC1 family members through a novel tyrosine repeat motif. Nucleic Acids Research 33(19): 6393–6404
Luo J, Li M, Tang Y, Laszkowska M, Roeder RG, Gu W (2004) Acetylation of p53 augments its site-specific DNA binding both in vitro and in vivo. PNAS 101(8) 2259–2264
Ma H, Nguyen C, Lee KS, Kahn M (2005) Differential roles for the coactivators CBP and p300 on TCF/beta-catenin-mediated survivin gene expression. Oncogene 24(22): 3619–3631
Markham D, Munro S, Soloway J, O’Connor DP, La Thangue NB (2006) DNA-damage-responsive acetylation of pRb regulates binding to E2F-1. EMBO Rep.7(2): 192–198
Martin C, Zhang Y (2005) The diverse functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6(11): 838–849
Martínez-Balbás MA, Bauer UM, Nielsen SJ, Brehm A, Kouzarides T (2000) Regulation of E2F1 activity by acetylation. EMBO J 19(4): 662–671
Maruta H, Greer K, Rosenbaum JL (1986) The acetylation of alpha-tubulin and its relationship to the assembly and disassembly of microtubules. J Cell Biol 103(2): 571–579
Marzio G, Wagener C, Gutierrez MI, Cartwright P, Helin K, Giacca M. (2000) E2F family members are differentially regulated by reversible acetylation. J Biol Chem 275(15): 10887–10892
Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Aoyama H, Yoshimochi K, Fukamizu A (2005) Acetylation of Foxol alters its DNA-binding ability and sensitivity to phosphorylation. PNAS 102(32): 11278–11283
McBryant SJ, Adams VH, Hansen JC (2006) Chromatin architectural proteins. Chromosome Res 14(1): 39–51
McMahon C, Suthiphongchai T, DiRenzo J, Ewen ME (1999) P/CAF associates with cyclin D1 and potentiates its activation of the estrogen receptor. PNAS 96(10) 5382–5387
Merika M, Thanos (2001) DEnhanceosomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11: 205–208
Munshi N, Agalioti T, Lomvardas S, Merika M, Chen G, Thanos D (2001) Coordination of a transcriptional switch by HMGI(Y) acetylation. Science 293: 1133–1136
Murphy PJ, Morishima Y, Kovacs JJ, Yao TP, Pratt WB (2005) Regulation of the dynamics of hsp90 action on the glucocorticoid receptor by acetylation/deacetylation of the chaperone. J Biol Chem 280(40): 33792–33799
Nishikawa K, Kobayashi M, Masumi A, Lyons SE, Weinstein BM, Liu PP, Yamamoto M (2003) Self-association of gatal enhances transcriptional activity in vivo in Zebra Fish embryos. Mol Cell Biol 23(22): 8295-8305
Olaharski AJ, Rine J, Marshall BL, Babiarz J, Zhang L, Verdin E, Smith MT (2005) The Flavoring agent dihydrocoumarin reverses pigenetic silencing and inhibits sirtuin deacetylases. PLoS Genet 1(6):e77
Ott M, Schnolzer M, Garnica J, Fischle W, Emiliani S, Rackwitz HR, Verdin E (1999) Acetylation of the HIV-1 Tat protein by p300 is important for its transcriptional activity. Curr Biol 16–30:9(24): 1489–1492
Pagans S, Pedal A, North BJ, Kaehlcke K, Marshall BL, Dorr A, Hetzer-Egger C, Henklein P, Frye R, McBurney MW, Hruby H, Jung M, Verdin E, Ott M (2005) SIRT1 regulates HIV transcription via Tat deacetylation. PLoS Biol 3(2):e41
Paranjape SM, Krumm A, Kadonaga JT (1995) HMG17 is a chromatin-specific transcriptional coactivator that increases the efficiency of transcription initiation. Genes Dev 9(16): 1978–1991
Qing Lu, Amanda E Hutchins, Colleen M Doyle, James R. Lundblad, Roland PS. Kwok (2001) Acetylation of cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) by CREB-binding protein enhances CREB-dependent Transcription. Mol Cell Biol 21(18): 6181–6188
Ramanathan B, Smerdon MJ (1986) Changes in nuclear protein acetylation in u.v.-damaged human cells. Carcinogenesis 7(7): 1087–1094
Rampalli S, Pavithra L, Bhatt A, Kundu TK, Chattopadhyay S (2005). Tumor suppressor SMAR1 mediates cyclin D1 repression by recruitment of the SIN3/histone deacetylase 1 complex. Mol Cell Biol 25(19) 8415–8429
Ruiz-Carrillo A, Wangh L, Allfrey V (1975) Assembly of newly replicated chromatin. Science 190(4210): 117–128
Sadri-Vakili G, Cha JH (2006) Mechanisms of Disease: Histone modifications in Huntington’s disease. Nature Clinical Practice Neurology, 2(6):330–338
Sakaguchi K, Herrera JE, Saito S, Miki T, Bustin M, Vassilev A, Anderson CW, Appella E (1998) DNA damage activates p53 through a phosphorylation-acetylation cascade. Genes Dev 12(18) 2831–2841
Shikama N, Chan HM, Krstic-Demonacos M, Smith L, Lee CW, Cairns W, La Thangue NB (2000). Functional interaction between nucleosome assembly proteins and p300/CREB-binding protein family coactivators. Mol Cell Biol 20(23): 8933–8943
Smith S, Stillman B (1991) Stepwise assembly of chromatin during DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J 10(4): 971–980
Solomon JM, Pasupuleti R, Xu L, McDonagh T, Curtis R, DiStefano PS, Huber LJ (2006) Inhibition of SIRT1 catalytic activity increases p53 acetylation but does not alter cell survival following DNA Damage. Mol cell Biol 26(1): 28–38
Sterner DE, Berger SL (2000) Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbioloby and Molecular Biology Reviews 64(2): 435–459
Sun Y, Jiang X, Chen S, Fernandes N, Price BD (2005) A role for the Tip60 histone acetyltransferase in the acetylation and activation of ATM. PNAS 102(37): 13182–13187
Swaminathan V, Kishore AH, Febitha KK, Kundu TK (2005) Human histone chaperone nucleophosmin enhances acetylation-dependent chromatin transcription. Mol Cell Biol 25(17) 7534–7545
Szczesny B, Bhakat KK, Mitra S, Boldogh I (2004) Age-dependent modulation of DNA repair enzymes by covalent modification and subcellular distribution. Mech Ageing Dev 125(10–11): 755–765
Tagami H, Péloponèse JM, Loret E, Jeang KT, Nakatani y, Emiliani S, Benkirane M, Kiernan RE (2002) Differential acetylation of Tat coordinates its interaction with the co-activators cyclin T1 and PCAF. EMBO J 21(24): 6811–6819
Van der Horst A, Tertoolen LG, de Vries-Smits LM, Frye RA, Medema RH, Burgering BM (2004) FOXO4 is acetylated upon peroxide stress and deacetylated by the longevity protein hSir2(SIRT1). J Biol Chem 279(28) 28873–28879
Varier RA, Kundu TK (2006) Chromatin modifications (acetylation/ deacetylation/ methylation) as new targets for HIV therapy. Curr Pharm Des 12(16): 1975–1993
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, Imai SI, Frye RA, Pandita TK, Guarente L, Weinberg RA (2001) hSIR2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell. Oct 19(107) 2149–159
Vo N, Fjeld C, Goodman RH. (2001) Acetylation of nuclear hormone receptor-interacting protein RIP140 regulates binding of the transcriptional corepressor CtBP. Mol cell Biol 21(18): 6181–6188
Wang X, Taplick J, Geva N, Oren M (2004) Inhibition of p53 degradation by Mdm2 acetylation. FEBS Lett 561(1–3): 195–201
Warnock LJ, Raines SA, Mee TR, Milner J (2005) Role of phosphorylation in p53 acetylation and PAb421 epitope recognition in baculoviral and mammalian expressed proteins. FEBS Journal 272(7): 1669–1675
Yamaguchi Y, Kurokawa M, Imai Y, Izutsu K, Asai T, Ichikawa M, Yamamoto G, Nitta E, Yamagata T, Sasaki K, Mitani K, Ogawa S, Chiba S, Hirai H (2004) AML1 is functionally regulated through p300-mediated acetylation on specific lysine residues. J Biol Chem 279(15): 15630–15638
Yoon S, Seger R (2006) The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors. 24(1): 21–44
Zhang Q, Yao H, Vo N, Goodman RH (2000) Acetylation of adenovirus EIA regulates binding of the transcriptional corepressor CtBP. PNAS 97(26): 14323–14328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Batta, K., Das, C., Gadad, S., Shandilya, J., Kundu, T.K. (2007). Reversible Acetylation Of Non Histone Proteins. In: Kundu, T.K., et al. Chromatin and Disease. Subcellular Biochemistry, vol 41. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-5466-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-5466-1_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-5465-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-5466-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)