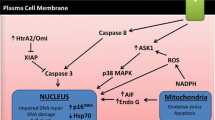
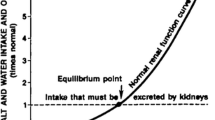
Abstract
The concept that a high salt intake is related to increased prevalence of hypertension is an old one. There is enough epidemiological, clinical, historical and experimental evidence to support this concept [1–3]. Most authorities currently believe that excessive salt intake is the first environmental risk factor for hypertension [4]. It appears that approximately one out of four normotensive subjects and one-half of all hypertensive patients are sensitive to salt, with their blood pressure increasing following excessive salt intake [5–7].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morgan T, Gilles A, Morgan G, Adam W, Wilson M, Carney S. Hypertension treated by salt restriction. Lancet, 1978, i: 227–230.
McGregor GA, Markandu N, Best FE, et al. Double-blind randomized cross-over trial of a moderate sodium restriction in essential hypertension. Lancet 1982, i: 351–355.
Hollenberg NK, Williams GH. Sodium-sensitive hypertension. Implication of pathogenesis for therapy. Am J Hyperten 1989; 2: 809–815.
Horan MJ, Lenfant C. Epidemiology of blood pressure and predictors of hypertension. Hypertension 1990 15(Suppl 1): 10-1–24.
Dahl LK. Metabolic aspects of hypertension. Ann Rev Med 1963; 14: 69–98.
Kawasaki T, Delea CS, Batter FC, Smith H. The effect of high-sodium and low-sodium intakes on blood pressure and other related variables in human subjects with idiopathic hypertension. Am J Med 1978; 68: 193–198.
Fujita T, Henrt WL, Batter FC, Lake CR, Delea CS. Factors influencing blood pressure in salt-sensitive patients with hypertension. Am J Med 1980; 69: 334–344.
Lindpaintner K, Sen S. Role of sodium in hypertensive cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res 1985; 57: 1610–1617.
Tobian L. Salt and hypertension lessons from animal models that relate to human hypertension. Hypertension 1991; 117(Suppl. 1): 1152–1158.
Safar ME, Bouthier JA, Levenson JA, Simon AC. Peripheral large arteries and the response to antihypertensive treatment. Hypertension 1983; 5(Suppl 3): 63–68.
Haddy FJ. The role of a humoral Na+, K+-ATPase inhibitor in regulating precapillary vessel tone. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1984; 6: S439–S456.
Brading AF, Lategan TW. Editorial review: Na-Ca exchange in vascular smooth muscle. J Hypertens 1985; 13: 109–116.
Clausen T. Adrenergic control of Na+ K+ homeostasis. Acta Med Scand 1983; 672 (Suppl): 111–115.
Benetos A, Breshahan M, Gavras I, Gavras H. Central catecholamines and alpha-adrenore-ceptors in acute hypertension induced by intracerebroventricular hypertonic saline. J Hypertens 1987; 5: 767–771.
McGregor GA, de Wardener HE. A circulation sodium transport inhibitor and essential hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1984; 6: S55–S60.
O’Rourke MF. Arterial function in health and disease. Edinburgh: Churchill Livinstone 1982: 324–357.
Roberts J ed. Blood pressure levels of persons 6-74 years. United states 1971–74. Department of Health. Education and Welfare publication No. HRA 78. Washington DC: United States Government Printing Office 1977.
Oliver WJ. Sodium homeostasis and low blood pressure populations. In: Kesteloot H, Joosens JV, editors. Epidemiology of arterial pressure. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff, 1980: 229–241.
Avolio AP, Deng FQ, Li WQ, et al. Effects of aging on arterial distensibility in populations with high and low prevalence of hypertension: comparison between urban and rural communities in China. Circulation 1985; 71: 202–210.
Avolio AP, Clyde CM, Beard TC, Cooke HM, Kenneth KL, O’Rourke MF. Improved arterial distensibility in normotensive subjects on a low salt diet. Arteriosclerosis 1986; 16: 166–169.
Benetos A, Yang-Yan X, Cuche JL, Hannaert P, Safar M. Arterial effects of salt restriction in hypertensive patients. A 2-month randomized double-blind, cross-over study. J Hypertens 1992; 10: 355–360.
Myers JB, Morgan TO. The effect of sodium intake on the blood pressure related to age and sex. Clin Exp Hypertens 1983; 5: 99–118.
Levenson JA, Simon AC, Maarek BE, Gitelman GJ, Fiessinger JN, Safar ME. Regional compliance of brachial artery and saline infusion in patients with arteriosclerosis obliterans. Arteriosclerosis 1985; 5: 80–87.
Dahl LK, Heine M, Tassinari L. Role of genetic factors in susceptibility to experimental hypertension due to chronic excess salt ingestion. Nature 1962; 194: 480–482.
Ganguli M, Tobian L, Iwai J. Cardiac output and peripheral resistance in strains of rats sensitive and resistant to NaCl hypertension. Hypertension 1979; 1: 3–7.
Racz K, Kuchel O, Buu NT. Abnormal adrenal catecholamine synthesis in salt-sensitive dahl rats. Hypertension 1987; 9: 76–80.
Chen YF, Meng Q, Wyss JM, Jin H, Rogers CF, Oparil S. NaCl does not affect hypothal-amic noradrenergic input in deoxycorticosterone acetate/NaCl and Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension 1987; 9: 76–80.
Ferrarie AU, Mark AL. Sensitization of aortic baroreceptors by high salt diet in dahl salt-resistant rats. Hypertension 1987; 10: 55–60.
Rapp JP. Dahl salt-susceptible and salt-resistant rats. Hypertension 1982; 4: 1753–1763.
Kong JQ, Taylor DA, Fleming WW, Kotchen TA. Specific supersensitivity of the mesenteric vascular bed of Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension 1991; 17: 1349–1356.
Lischer TF, Raij, Van Houtte PM. Endothelium-dependent vascular responses in normotensive and hypertensive Dahl rats. Hypertension 1987; 9: 1-57–63.
Benetos A, Bouaziz H, Safar M. Endogenous bradykinin activity in Dahl rats. J CV Pharmacol 1993; 21: 101–104.
Boegehold M, Kotchent T. Effect of dietary salt on the skeletal muscle microvascularture in Dahl rats. Hypertension 1990; 15: 420–426.
Lee RMKW, Triggle CR. Morphometric study of mesentereic arteries from genetically hypertensive Dahl strain rats. Blood Vessels 1986: 23: 199–224.
Tobian L, Lange J, Iwai J, Hiller K, Johnson MA, Grossen P. Prevention with thiazide of NaCl-induced hypertension in Dahl ”S“ rats. Hypertension 1979; 1: 316–323.
Bouaziz H, Benetos A, Levy BI, Safar ME. Arterial mechanical properties of Dahl sensitive rats. In: Sassard J, editor. Genetic Hypertension. Colloque INSERM 1992; 218: 273–275.
Bouaziz H, Benetos A, Albaladejo P, Guez, Safar ME. Arterial mechanical properties of Dahl sensitive rats: effects of indapamide. (Submitted for publication.)
Benetos A, Bouaziz H, Albaladejo P, Levy BI, Safar ME. Physiological and pharmacological changes in the carotid artery pressure-volume in situ in rats. J Hypertens 1992; 10(Suppl 6): S127–S131.
Draaijer P, Kool M, Van Bortel L, De Leeuw P, Leunissen KML. Salt sensitive borderline hypertensive patients (SRBHT vs SSBHT). J Hypertens 1992; Vol. 10(Suppl 4): 74 (Abstract).
Uehara Y, Numabe A, Hirawa N, et al. Antihypertensive effects of cicletanine and renal protection in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J Hypertens 1991; 9: 1719–1728.
Schini VB, Dewey J, Van Houtte PM. Effects of indapamide on endothelium-dependent relaxations in isolated canine femoral arteries; Am J Cardiol 1990; 65: 6H–10H.
Uehara Y, Shirahase H, Nagata T, et al. Radical scavenging effects of indapamide on prostacyclin generation in vascular smooth muscle cells in rats. Hypertension 1990; 15: 216–224.
Levy BI, Poitevin P, Safar M. Effects of Indapamide on the mechanical properties of normotensive and hypertensive rats without arterial pressure changes. J Card Pharmacol 1989; 14: 253–259.
Kraetz J, Criscione L, Hedwal PR. Dissociation of vascular and natriuretic effects of diuretic agents. Naumyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 1978; 302 (Suppl) R42.
Levy BI, Curmi P, Poitevin P, Safar ME. Modifications of the arterial mechanical properties of normotensive and hypertensive rats without arterial pressure changes. J Cardio Pharmacol 1989; 14: 253–259.
Asmar R, Benetos A, Chaouche K, Raveau-Landon C, Safar M. Arterial changes following diuretic therapy versus calcium blockade hypertension. 14e Scientific Meeting of the International Society of Hypertension.(Abstract), Madrid 1992.
Carretta R, Fabris B, Bardelli M, et al. Arterial compliance and baroreceptor sensitivity after chronic treatment with indapamide. J Human Hypertension 1988; 2: 171–175.
Laurent S, Lacolley PM, Cuche JL, Safar ME. Influence of diuretics on brachial artery diameter and distensibility in hypertensive patients. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 1990; 4: 685–693.
Smulyan H, Vardan S, Griffiths A, Gribbin B. Forearm arterial distensibility in systolic hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 1984; 3: 387–393.
Laurent S, Hannaert PA, Girerd XJ, Safar ME, Garay R. Chronic treatment with canrenone potentiates the acute pressor effects of ouabain in essential hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 1987; 5(Suppl 5): SI S73–S75.
Safar ME, Levy BI, Laurent S, London GM. Hypertension and the arterial system: clinical and therapeutic aspects. J Hypertens 1990; 8(Suppl 7): S113–S119.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1993 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Benetos, A., Safar, M.E. (1993). Large arteries and sodium in hypertension. In: Safar, M.E., O’Rourke, M.F. (eds) The Arterial System in Hypertension. Developments in Cardiovascular Medicine, vol 144. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0900-0_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0900-0_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-4389-2
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-0900-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive